Overview
OPC Unified Architecture (OPC UA) is a standard pushed by the OPC Foundation for industry automation. The goal of OPC UA is to enable the communication between industrial devices. OPC UA is designed to work across technology boundaries (cross-platform). There are two components designed to accomplish this integration:
- OPC UA device gateway
- OPC UA management service
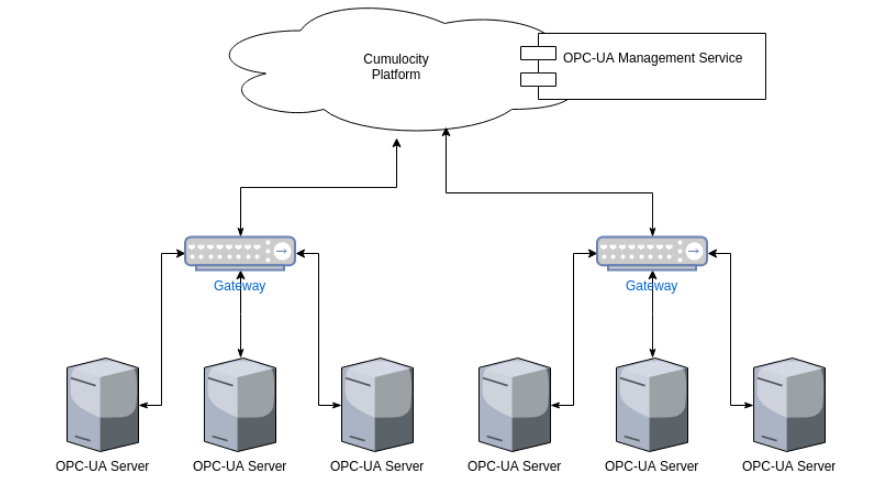
The OPC UA device gateway is a stand-alone Java program that communicates with OPC UA server(s) and the Cumulocity IoT platform. It stores data into the Cumulocity IoT database via REST. Additionally, C8Y commands are executed to perform various operations on the OPC UA servers.
The gateway must be registered as Cumulocity IoT device in a specific tenant and the opcua-device-gateway must run in the users' environment.
To download the gateway navigate to Cumulocity IoT resources.
The gateway requires Java 11 in order to run.
Gateway configuration and registration
YAML file and spring profiles are used for the configuration of the gateway. A default configuration file is embedded in the gateway JAR file, so you only must set the properties which are different from the default.
To run the gateway locally, the default settings should be overridden in a customized profile. To use the customized profile, create a YAML file which must follow the naming convention:
application-<<Profile_name>>.yaml
For example, to connect to a tenant, first a profile named application-myTenant.yaml will be created. The following properties will be added to the file:
C8Y:
baseUrl: https://<<yourTenant>>.cumulocity.com
gateway:
bootstrap:
tenantId: <<yourTenantId>>
identifier: Gateway_Device
name: My Gateway
db:
# The gateway uses the local database to store platform credentials and local cache. This parameter shows the location in which the local data should be stored.
baseDir: C:/Users/<<userName>>/.opcua/data
Configuration profile location on the filesystem
The configuration profile can be stored either in the same directory as the JAR file or in a default configuration directory. Depending on the operating system, the following default configuration directories can be used:
Windows OS
/C:/opcua/
Linux OS
/etc/opcua/
/etc/opcua/data
Mac OS
/opt/opcua/
/opt/opcua/data
The number of profiles you may have is not limited. To use a specific profile on runtime, the “–spring.profiles.active” JVM argument must be passed when running the gateway JAR file. For example, let’s use the previously created profile. Start a terminal and use the following command:
java -jar opcua-device-gateway-<<version>>.jar --spring.profiles.active=default,myTenant
The command above will start a gateway with the default profile and it will override the default properties with the properties defined in the “myTenant” profile. The list of profiles must be provided as an ordered, comma-separated list. The default profile always needs to be the first profile in the list.
Optional: To specify your own configuration, Spring arguments can be used in your terminal to run the gateway JAR file. Multiple locations must be comma-separated. The configuration locations should be either YAML files or directories. In case of directories, they must end with “/”. For example:
java -jar opcua-device-gateway-<<version>>.jar --spring.config.location=file:<<location>>/.opcua/conf/application-myTenant.yaml,file:<<location>>/.opcua/conf/
If both arguments “–spring.config.location” and “–spring.profiles.active” are provided, the configuration locations should be directories instead of files. Otherwise, the profile-specific variants will not be considered.
Additional customizations
The following properties can be manually configured in the YAML file:
# Name of the application - this should not change
name: opcua-device-gateway
# Platform location and configuration
C8Y:
# This is the base URL pointing to the Cumulocity IoT platform. This must always be customized in an application profile.
baseUrl: http://localhost
# This is an internal setting of the Cumulocity IoT SDK. It is set to true, because we typically
# want to configure the Cumulocity IoT SDK to always use the baseURL provided during initialization.
# Otherwise, the gateway would use the links in the `self` fragment of the core API responses as the host name.
# This is helpful in deployment scenarios where the Cumulocity IoT instance is
# reachable only with an IP address.
forceInitialHost: true
#
# Gateway-specific settings
#
gateway:
# The version of the gateway - this is filled automatically during the build process - do not change this property
version: ${project.version}
# The following two properties will be set to the name of the user that is running the gateway unless it's overridden manually
identifier: mygateway
name: mygateway
# The gateway uses a local database to store platform credentials and a local cache. This setting tells
# where local data is stored.
db:
baseDir: ${user.home}/.opcua/data
addressSpace:
# Starting from version 10.11, the opcua-device-gateway process creates the address space local db files are with a new filename
# (cumulocity-opcua-server-<serverId>-address-space-pv4.bin) due to a dependency change to avoid conflicts.
# The legacy address space local db files can be cleaned up at the start of the opcua-device-gateway process
# automatically when the legacyCleanup is set to true, which is the default setting.
# If the legacy files wanted to be kept or if the mechanism for clearing is not needed, set legacyCleanup to false.
legacyCleanup: true
# These settings control the device bootstrap process of the gateway.
# In general, the default settings are sufficient, and should not be changed.
# Contact product support (https://cumulocity.com/guides/<latest-release>/welcome/contacting-support/)
# in case the bootstrap credentials are different.
bootstrap:
# Tenant ID to be used for device bootstrap
tenantId: management
# Credentials for the device bootstrap user
username: devicebootstrap
password: <devicebootstrap user password>
# When the gateway starts, it waits <delay> milliseconds before connecting to the platform and searching for
# the device.
delay: 5000
# If set to true, the gateway will drop any stored device credentials and fetch new ones from the platform.
force: false
# Scheduled tasks and thread pools configuration
# Only change the settings here if really necessary. Wrong scheduler configurations can
# disturb the gateway's operation.
scheduler:
# Threadpool specific settings
threadpool:
# This setting corresponds to the size of the threadpool used for periodic tasks.
size: 15
# These settings control the threadpool of our internal task executor, which is used for generic background
# execution and asynchronous tasks.
executor:
threadpool:
coreSize: 30
maxSize: 60
# The following settings control the settings of the device type mappings execution.
mappingExecution:
# This section contains all settings related to external, custom-action execution.
http:
# Connection request timeout (milliseconds)
connectionRequestTimeout: 3000
# Connection timeout (milliseconds)
connectionTimeout: 3000
# Socket timeout (milliseconds)
socketTimeout: 5000
# Maximum number of connections via HTTP route
maxPerRoute: 100
# Maximum total size of the HTTP connection pool used for external, custom actions.
maxTotal: 100
# The inactivityLeaseTimeout setting defines a period, after which persistent connections to
# the HTTP server must be reevaluated. See PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager for more information
inactivityLeaseTimeout: 50000 #ms
# Aggregate number of alarms if something goes wrong with the execution of external custom actions
failureAlarmAggregate: true
# How often is the alarm aggregation for failed external calls invoked?
failureAlarmFixedDelay: 15 # seconds
failureHandling:
# Whether a failed HTTP POST should be retried later or not. This can be overridden by the configuration in device type. Default is false
enabled: false
# Number of retries a failed HTTP POST will be resent
maxRetries: 5
# If retry is enabled, the exceptions of HTTP status codes can be provided here, comma separated. A HTTP POST which failed with one of these codes will not be retried. This can be overridden by the configuration in the device type. Default is empty which means that all failed http posts will be retried if enabled. Example: 400,500
noRetryHttpCodes:
# Minimum delay in seconds between two retries
retryDelay: 120
# Max queue size of the HTTP POST actions queue
maxQueueSize: 50000
# Worker thread (which performs the actual HTTP request) pool size
threadPoolSize: 200
# Threadpool configuration for the mapping execution
# Each value arriving in the gateway will be handled by one or more action handlers defined in the device type. Each handler will be executed in one single thread.
# Hence, this threadpool must be large enough to cope with the parallel processing needs of values
# received from the OPC UA server.
threadpool:
size: 200
# To avoid many REST calls to the inventory an in-memory map with a crash backup functionality is included.
alarmStatusStore:
# Expected number of maximum alarms at the same time
maxEntries: 100000
# The average size of the keys on the map. Needed for calculation of the size of the database file.
averageKeySize: 30
# The number of maxEntries multiplied with this factor results in the real max size of the database file. Resize is done only if needed.
maxBloatFactor: 5.0
# Mapping-specific settings
mappings:
# In OPC UA, alarm severity is specified by an integer range between 0 and 1000. The alarmSeverityMap
# allows to configure how OPC UA severity is mapped into Cumulocity IoT severity levels. The following is the default mappings:
# alarmSeverityMap:
# 1001: CRITICAL
# 801: CRITICAL
# 601: MAJOR
# 401: MINOR
# 1: WARNING
# Mapping synchronization interval
# The OPC UA gateway periodically fetches the OPC UA device types. With the following settings, this
# interval can be adjusted.
# Sync interval in milliseconds. The default is 43200000ms (12 hours)
syncInterval: 43200000
# Operation settings
operation:
# Default behavior that controls if the OPC UA gateway performs an address space scan when it connects the first time to an OPC UA server. Can be overridden in the OPC UA Server config.
autoScanAddressSpace: true
# Cyclic-Reader settings
cyclicRead:
# The cyclic readers use a dedicated threadpool to perform periodic read tasks.
threadpool:
# Allows the size of the threadpool for cyclic reads to be configured
size: 30
# How many nodes can be read at once for the cyclic read of the same device protocol, server, root node and the same parameters (rate, max-age).
defaultBulkSize: 1000
# OPC UA subscription settings: These settings allow global OPC UA configuration parameters
# for subscription-based data reporting
subscription:
# The reporting rate (in milliseconds) corresponds to the publishing rate for monitored items.
reportingRate: 100
# The maxKeepAliveCount specifies the maximum number of OPC UA reporting intervals with no data that
# can be skipped before the OPC UA server sends an empty response to the gateway, informing about
# a yet active, but idle OPC UA subscription.
maxKeepAliveCount: 200
# The lifeTimeCount specifies the maximum number of reporting intervals without a value being sent.
# After the lifetime count has exceeded, the subscription is terminated.
# Must be 3 times greater than maxKeepAliveCount
lifetimeCount: 600
# The notificationBufferSize defines how many monitored item values should be buffered to receive
# subscription notification data from the OPC UA server. The subscription reporting rate (publish interval)
# and the volume of sampling data should be taken into account to choose a suitable buffer size.
notificationBufferSize: 500
# The recreateFailedItems flag can be used to enable the feature of a subscription so that it automatically retries to create the monitored items
# if they fail due to error code Bad_NodeIdUnknown. It assumes that the NodeIds are correct, but it hasn't been added to the
# server's address space yet. The default value is false.
recreateFailedItems: false
# Subscription update settings
subscriptionUpdate:
# The subscription update interval controls how often the OPC UA gateway updates the subscription
# settings for connected OPC UA servers. Expects: Interval duration in milliseconds.
interval: 60000
# Server connectivity configuration
connectivity:
# If the autoReconnect in the server's client configuration is set to false, then the gateway tries to reconnect manually.
# triggerManualReconnectOnConnectionDrop can be used to stop the manual reconnect as well if set to false. The default value is true.
triggerManualReconnectOnConnectionDrop: true
# Internal repository configurations
repositories:
# Interval in milliseconds describing how often the repositories are flushed to the platform
flushInterval: 10000
# Threadpool size for the event queue flushing
eventsThreadpool: 30
# Threadpool size for the alarm queue flushing
alarmsThreadpool: 30
# Threadpool for the measurement queue flushing
measurementsThreadpool: 60
# Maximum capacity. If a repository grows over this size, the OPC UA communication will be shut off!
maximumCapacity: 250000
# Re-enable threshold. If OPC UA communication has been disabled due to exceeding maximum capacity, this threshold
# controls when OPC UA communication is enabled again
reenableThresholdSize: 10
# The settings below describe platform-specific connection parameters.
platform:
inventory:
update:
# Default processing mode for inventory managed objects update to the Cumulocity IoT platform.
defaultProcessingMode: QUIESCENT
# Processing mode for inventory update of the gateway device managed objects to the Cumulocity IoT platform.
gateway:
processingMode: QUIESCENT
# Processing mode for inventory update of the OPC UA server device managed objects to the Cumulocity IoT platform.
server:
processingMode: QUIESCENT
# Processing mode for inventory update of value-map managed objects to the Cumulocity IoT platform.
valuemap:
processingMode: QUIESCENT
# Connection pool configuration
connectionPool:
# Overall maximum size of the connection pool
max: 250
# Max connections used for a single host
perHost: 150
# Gateway self-monitoring configuration
# First, the gateway internally measures different metrics and populates them to the platform.
# Second, the gateway actively checks if a server connection is active and working by regularly
# browsing the root node of an OPC UA server.
monitoring:
# The interval below in milliseconds configures the frequency of this monitoring task.
interval: 10000
# The interval below in milliseconds configures how often we investigate the thread executor queue sizes to prevent overflow
checkQueueSizes: 10000
# The OPC UA gateway persists all latest values of an OPC UA server in a dedicated managed object,
# the so-called value map. These value maps are locally kept on the device for a certain time
# before being pushed to the platform, allowing for local aggregation of all last-seen values.
valueMap:
# The lifetime of a local value map in seconds
lifeTime: 30
# How often (in milliseconds) does the gateway check for changes in configured servers.
# This setting controls how long it takes for the gateway to discover an added or a removed server
childrenAddedOrRemoveCheck:
interval: 15000
# How often (in milliseconds and if enabled) the gateway reads pending operations from the platform.
shortPolling:
enabled: true
fixedDelay: 15000
# Time in days for which the certificate is valid.
applicationIdentity:
validityTime: 3650
# Timeout scanning address space in minutes
scanAddressSpace:
timeout: 1440
retries: 5
Logging
Custom logging configuration can be set during startup by passing the “–logging.config” JVM argument. For more info on how to set up custom logging settings, refer to the “Logback” documentation. A sample logging configuration file may look like this:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<configuration scan="true" scanPeriod="30 seconds">
<include resource="org/springframework/boot/logging/logback/defaults.xml" />
<appender name="FILE"
class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.RollingFileAppender">
<file>/${user.home}/.opcua/log/device-gateway.log</file>
<encoder>
<pattern>${FILE_LOG_PATTERN}</pattern>
</encoder>
<rollingPolicy class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.TimeBasedRollingPolicy">
<!-- rollover daily -->
<fileNamePattern>/${user.home}/.opcua/log/device-agent-%d{yyyy-MM-dd}.%i.log
</fileNamePattern>
<timeBasedFileNamingAndTriggeringPolicy
class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.SizeAndTimeBasedFNATP">
<maxFileSize>50MB</maxFileSize>
</timeBasedFileNamingAndTriggeringPolicy>
<maxHistory>5</maxHistory>
</rollingPolicy>
</appender>
<appender name="STDOUT" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender">
<encoder>
<pattern>${CONSOLE_LOG_PATTERN}</pattern>
<charset>utf8</charset>
</encoder>
</appender>
<logger name="com.cumulocity.opcua.client.gateway" level="INFO" />
<logger name="com.cumulocity" level="INFO" />
<logger name="c8y" level="INFO" />
<root level="INFO">
<appender-ref ref="FILE" />
<appender-ref ref="STDOUT" />
</root>
</configuration>
Deletion of gateway
An OPC UA gateway can be associated with multiple OPC UA servers, and the servers can have multiple child devices connected to them. The cleanest approach to delete a gateway is to first delete the OPC UA server managed objects and all its child devices.
The server can be either deleted from the OPC UA server tab of the gateway (recommended way of deletion), or from the device list itself. If the server is deleted from the OPC UA server tab, then the server managed object and all the address space managed objects are deleted by the OPC UA management service, but the child devices associated with the server must be deleted separately.
On the other hand, if the server is deleted from the device list, then the child devices associated with the server can be deleted by selecting the checkbox Also delete child devices of this device. The deletion is detected by the gateway, and the address space managed objects are deleted for the corresponding server. If the gateway is offline, then the address space managed objects will not be removed.
The process of deletion is asynchronous for both cases, so it may take a while to completely remove all the associated managed objects. Thereafter, the gateway can be deleted from the list of devices along with the device user by selecting the checkbox Also delete associated device owner “device_<gateway_name>".
If the gateway is directly deleted from the list of devices before deleting gateway’s servers and devices of those servers, by selecting the checkbox Also delete child devices of this device, then the server managed object will be deleted, but the corresponding address space objects will not be deleted as they are not children of the gateway.
Downgrade to an earlier version
Due to security improvements, downgrades from 10.12.0 to previous versions are not directly supported. However, if required, a downgrade is possible by following the instructions below:
- Shut down the current version of the gateway and remember the gateway managed object ID from the devices list.
- Send an HTTP PUT command to your tenant to reset the identity:
PUT {url_to_your_tenant}/inventory/managedObjects/{device_id}
{
"c8y_ua_IdentityConfig":null
}
- The response code should be 200 OK.
- Start the old version of the gateway.
After completing these steps a new identity will be created in the old structure.
It is possible to upgrade to version 10.12.0 or above at a later stage. The necessary conversion will be done automatically.
Running the Gateway
The gateway can run with either default or custom settings. To run the gateway run one of the commands below:
-
Default settings and default logging configuration:
java -jar opcua-device-gateway-<<version>>.jar -
Custom settings and default logging configuration:
java -jar opcua-device-gateway-<<version>>.jar --spring.profiles.active=default,PROFILE_NAME -
Custom settings and custom logging configuration:
java -jar opcua-device-gateway-<<version>>.jar --spring.profiles.active=default,PROFILE_NAME --logging.config=file:PATH_TO_LOGBACK_XML
For example, using the profile from the previous section we are going to register the gateway. First, open the terminal and navigate to the location of the gateway.jar file. Next, enter the following command:
java -jar opcua-device-gateway-<<version>>.jar --spring.profiles.active=default,myTenant
Adjusting gateway memory settings
In certain scenarios it is required to adjust the memory settings of the gateway application. Examples for such scenarios are the integration of servers with very large address spaces or obtaining large amounts of data from servers using high sampling rates.
You can adjust the memory settings of the gateway like with any other Java program. Typically, it is sufficient to increase the initial heap size and the maximum heap size of the gateway process.
-
Example: Run the gateway with a minimum heap size of 2 GB and a maximum heap size of 8 GB.
java -Xms2g -Xmx8g -jar opcua-device-gateway-<<version>>.jar
Performance tuning for large setups
If you’re running your setup with a large number of connected OPC UA servers the scan of these nodes can take a long time and may fail with the default settings. There are a lot of other problems like data collection and synchronisation, subscriptions, cyclic reads and flushing data. We recommend you to tune the following settings in the configuration YAML file (values are just examples of a known large setup):
gateway:
scheduler:
threadpool:
size: 300
executor:
threadpool:
coreSize: 600
maxSize: 1200
If cyclic read (only subscription) is used we recommend
cyclicRead:
threadpool:
size: 3000
otherwise size 0 is perfect.
In general, a larger number of threads will increase your performance. To increase the number of threads, add more memory.
Registering the gateway as a Cumulocity IoT device
-
Click Registration in the Devices menu of the navigator.
-
Click Register device at the right of the top bar and from the dropdown menu select Single registration > General.
-
Enter the Device ID (in our example it is “Gateway_Device”) and then click Next.
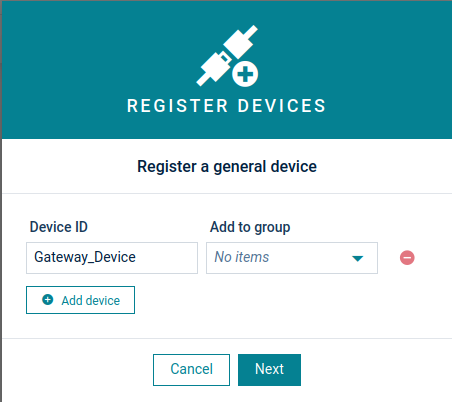
- Click Accept to complete the registration.
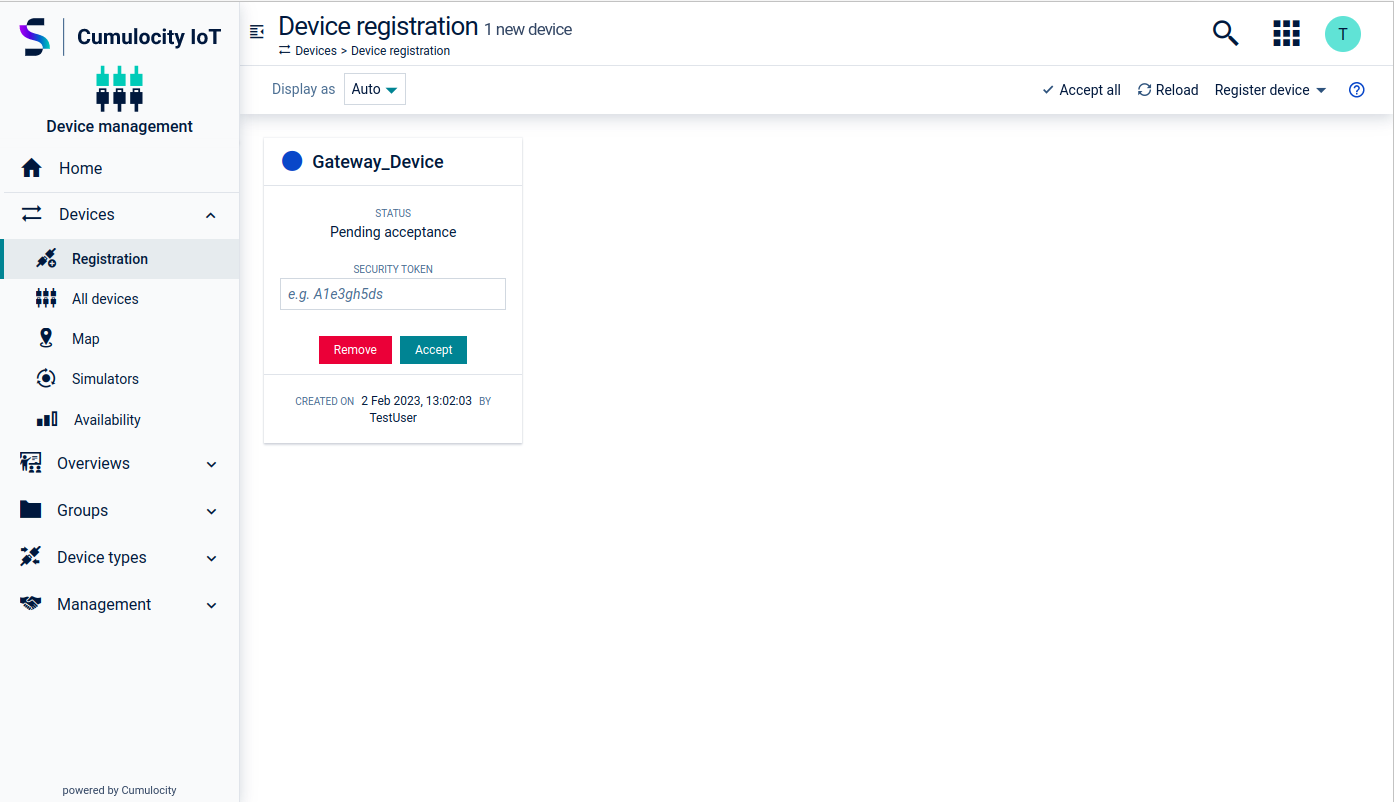
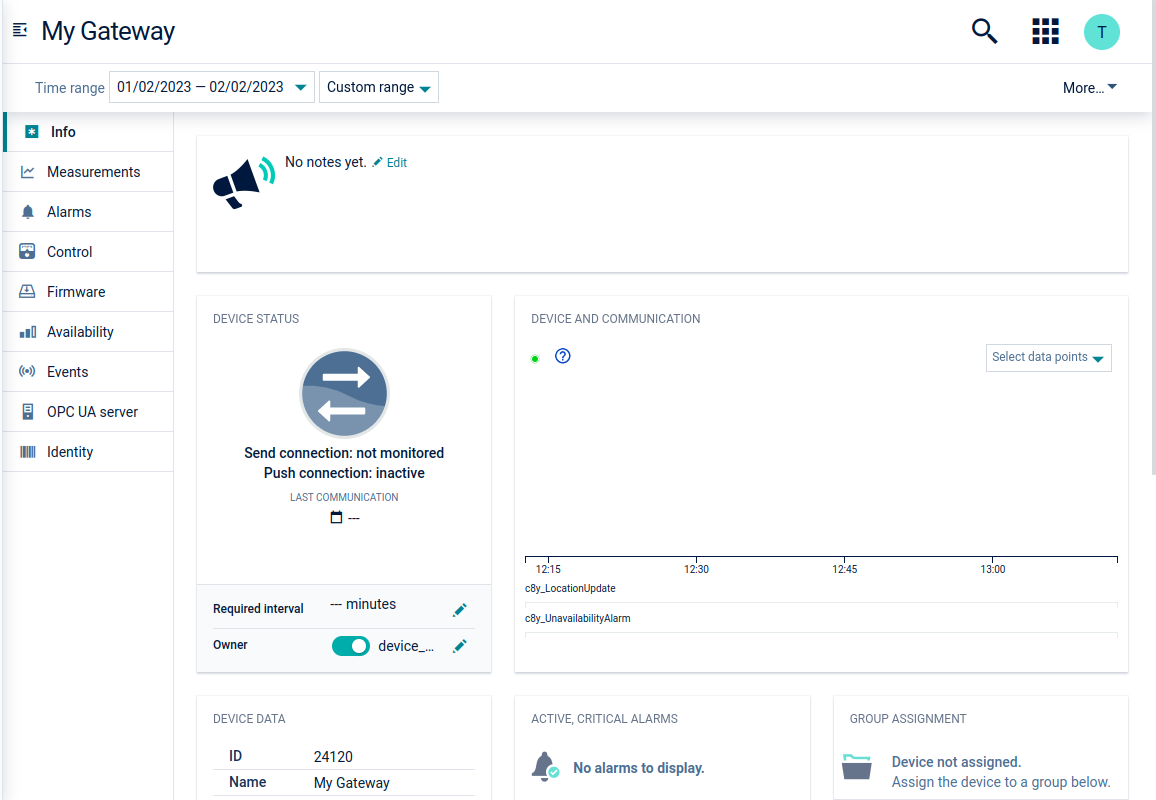
Gateway device details
After the registration is completed, the gateway device will be created by the opcua-device-gateway.
In this section, only OPC UA specific information related to the tabs in the device details page will be explained. For more info on all tabs, see Device Management > Device Details in the User guide.
Connecting the gateway to the server
Next, establish a connection between the gateway and the OPC UA server.
- In the OPC UA server tab of the respective gateway, click Add server.
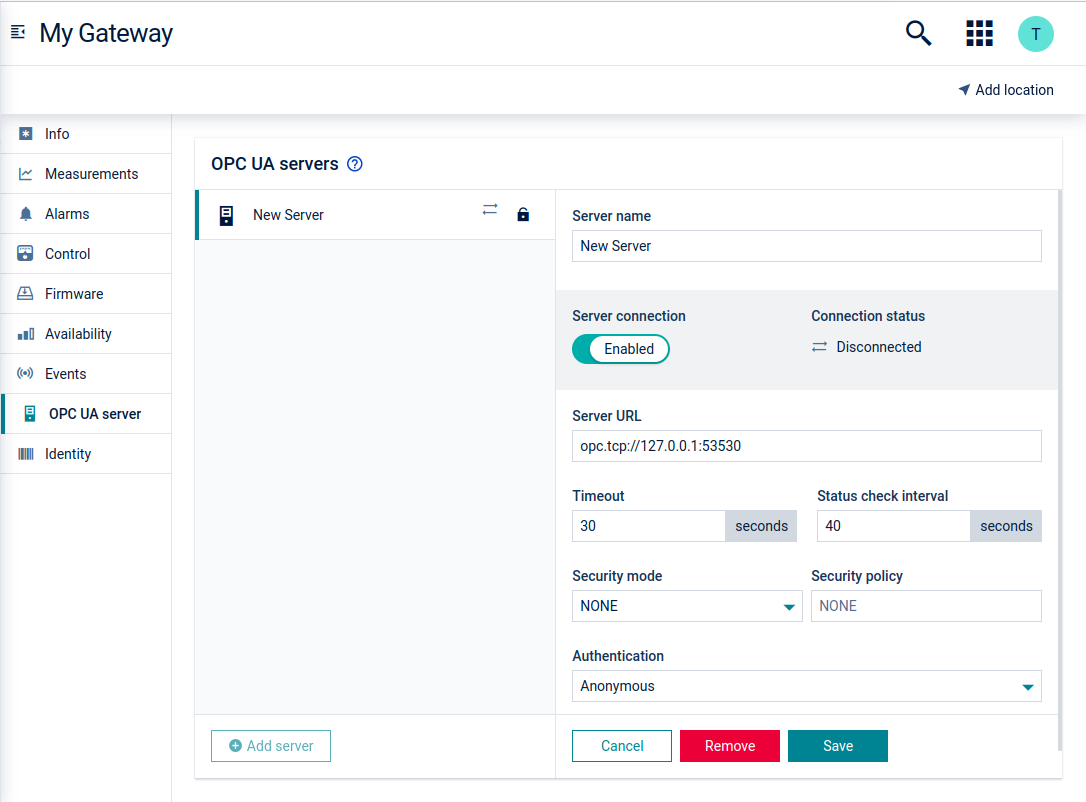
- Use the Server connection toggle, to enable or disable the server connection.
- Enter the Server URL which is used to establish a connection between the server and the gateway.
- Enter the Timeout value in seconds. The timeout value is calculated for each request. If the timeout value is exceeded the request will be unsuccessful.
- Enter the Status check interval in seconds. The status check interval specifies how often the gateway actively checks if the server status has changed. These periodic checks are carried out by reading the ServerStatus variable on the OPC UA server.
- Select the Security mode and Security policy depending on the server configuration. For more info, see Security modes.
- Select the desired authentication method. For more info, see Authentication.
- Click Save.
Security modes
The security mode settings tell the gateway how it should secure the connection between itself and the OPC UA server. When a mode other than NONE is selected, the gateway will auto-generate a self-signed application instance certificate and will use it to connect to the server. Possible security mode options are:
- NONE
- BASIC128RSA15_SIGN
- BASIC128RSA15_SIGN_ENCRYPT
- BASIC256_SIGN
- BASIC256_SIGN_ENCRYPT
- BASIC256SHA256_SIGN
- BASIC256SHA256_SIGN_ENCRYPT
Authentication
The authentication setting is used to authenticate and authorize the server user. It tells the gateway how to create a user identity and how to send it to the OPC UA server when establishing a connection.
The following authentication methods can be selected:
- Anonymous - Will only work when the OPC UA server allows such connections.
- Username/Password - With this setting the gateway will connect to the server as a specific user represented by a username and password.
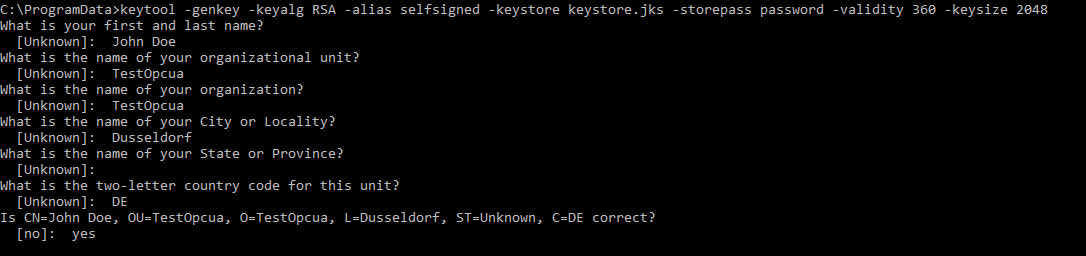
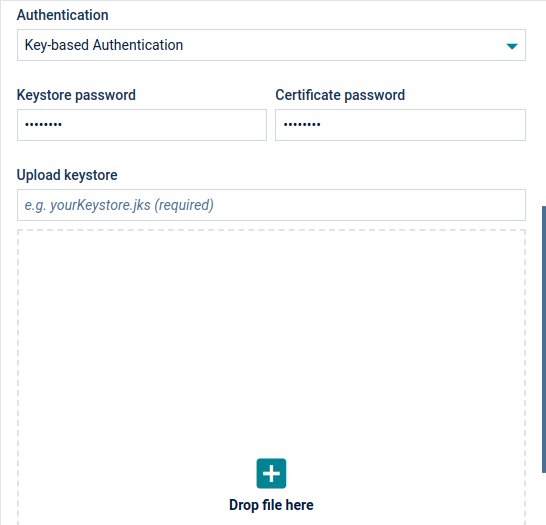
- Key-based authentication - The gateway will use an existing certificate to authenticate as a specific user. JKS keystore must be uploaded to Cumulocity IoT as a binary with type “application/octet-stream”. This keystore must follow the following rules:
- It must be a Java keystore (JKS).
- The keystore itself must be password-protected.
- The keystore must contain a user certificate with the “opcuauser” alias.
- The user certificate must be password-protected.
The keystore can be created via the following Java keytool command:
keytool -genkey -keyalg RSA -alias opcuauser -keystore keystore.jks -storepass passw0rd_a -validity 3600 -keysize 2048
With the above command, the key pass is set to the same value as the keystore password.
The keystore can be verified by using a tool like KeystoreExplorer. It can then be uploaded to Cumulocity IoT as a binary and used in the server configuration.
Child devices
All server connections are listed as child devices even if the servers are disconnected. To stop a server connection, either delete the server child device or disable/remove the connection from the OPC UA server tab.
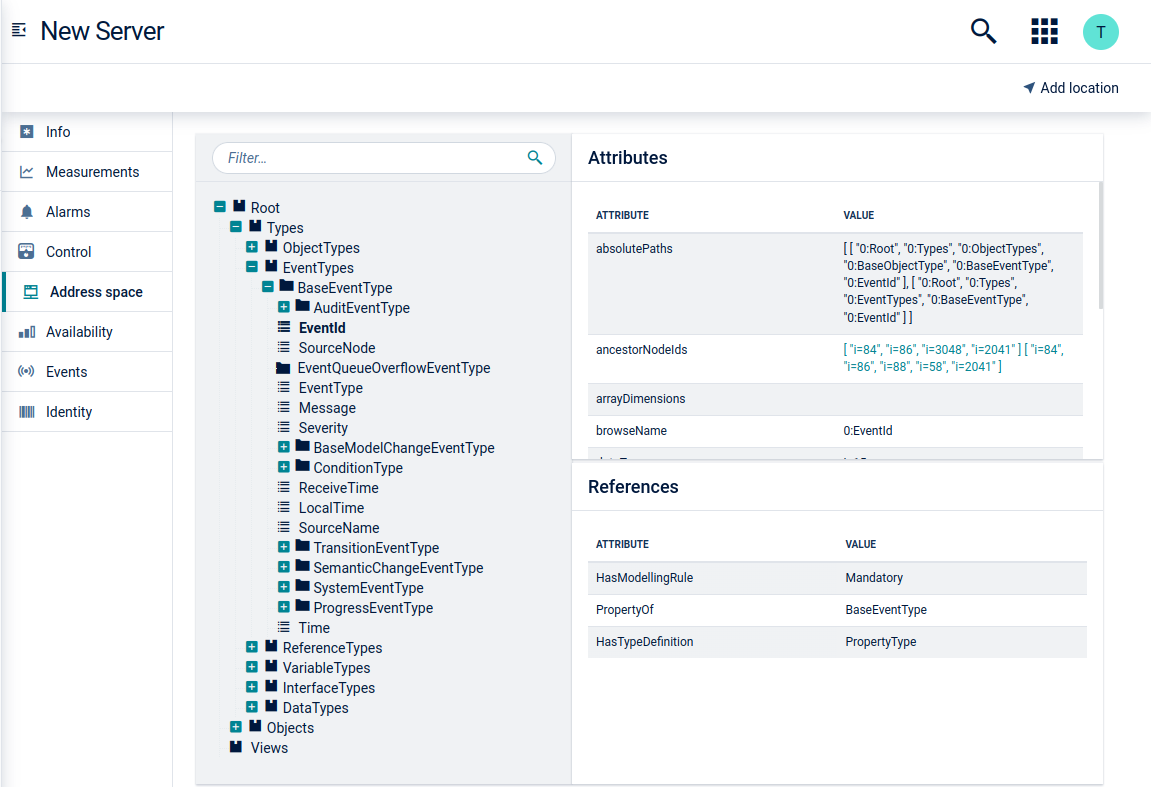
Address space
When you navigate to the child device of the gateway, the Address space tab shows the attributes and references of the address space node of the servers. The filter searches through the whole hierarchy to find “nodeId”, “browserName” or “displayName” of an attribute. In case of multiple “ancestorNodeIds”, you can click on the desired node to be redirected.
The address space is automatically scanned when a connection between the gateway and the server is established. The duration of the scan depends on the size of the address space. The address space information is stored locally once it is scanned and then used by this applying process. If the address space information is not yet available, for example, the address space has not been scanned, another scan will be triggered without synchronizing data into Cumulocity IoT. Performing another address space operation will update the address space information.
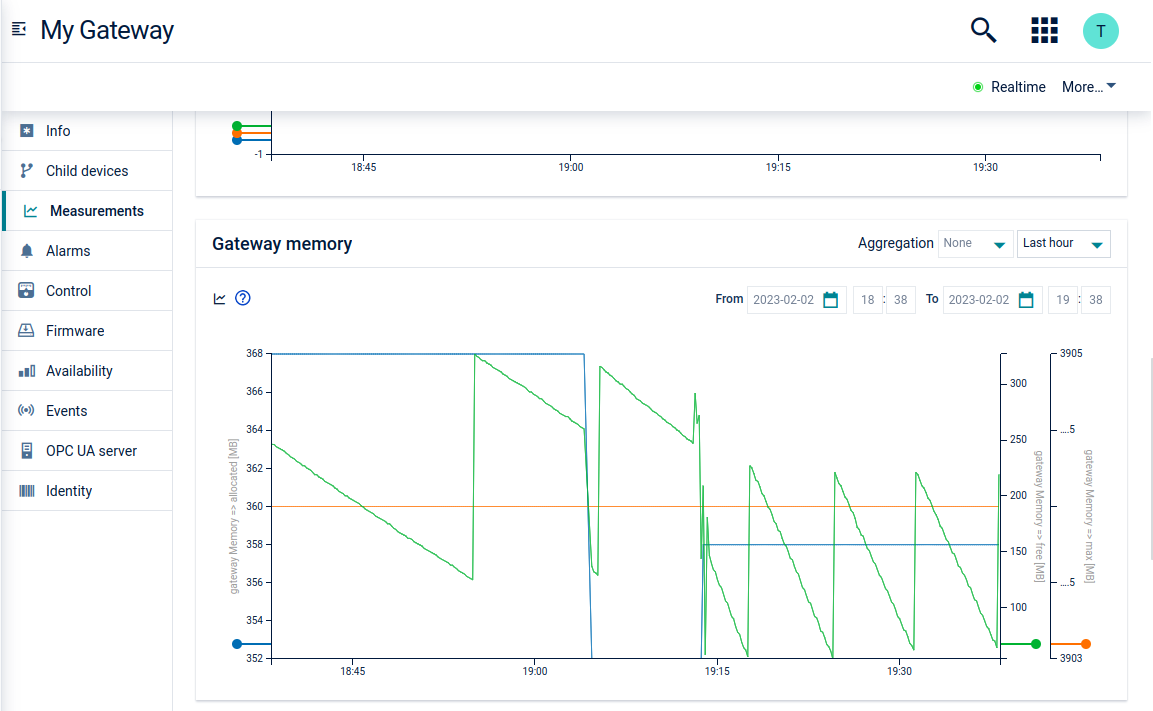
Monitoring measurements
On the gateway device, the Measurements tab provides visualization of data in the form of charts. In total the gateway contains the following six charts:
| Charts | Description |
|---|---|
| Connected servers | Provides the number of connected and disconnected servers. |
| Gateway active threads | Shows the number of active threads for the alarm/measurements/event flushes and for the executor. You can also see whether the threadpool size limit is not sufficient, based on the threadpool configurations in the gateway. If the maximum threadpool size is reached then any new activities which require a new thread will be blocked until a thread is available. |
| Gateway cyclic reads | Number of active cyclic reads done by the gateway. Cyclic reads are actively reading from the OPC UA server within an interval based on the configuration of the device protocol. |
| Gateway memory | Represents the "free", "max" and "allocated" memory values of the gateway. |
| Gateway repository queues | Before a thread is flushed it is first added to the queue. This chart shows how many threads are currently in the queue. |
| Server response time | Shows the response time of each currently connected server. |
Monitoring measurement details
The following is the full list of monitoring measurements created by the gateway:
| Chart | Measurement type | Measurement series | Unit | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Connected servers | c8y_connectedServers | connected servers | num | Number of connected servers |
| Connected servers | c8y_connectedServers | disconnected servers | num | Number of disconnected servers |
| Gateway active threads | c8y_gatewayActiveThreads | event_flush | threads | Number of active threads for event flushing |
| Gateway active threads | c8y_gatewayActiveThreads | alarm_flush | threads | Number of active threads for alarm flushing |
| Gateway active threads | c8y_gatewayActiveThreads | measurement_flush | threads | Number of active threads for measurement flushing |
| Gateway active threads | c8y_gatewayActiveThreads | event_flush_queued | threads | Number of queued threads for event flushing |
| Gateway active threads | c8y_gatewayActiveThreads | alarm_flush_queued | threads | Number of queued threads for alarm flushing |
| Gateway active threads | c8y_gatewayActiveThreads | measurement_flush_queued | threads | Number of queued threads for measurement flushing |
| Gateway cyclic reads | c8y_gatewayCyclicReads | scheduled_reads | scheduled | Number of cyclic reads that have been scheduled |
| Gateway cyclic reads | c8y_gatewayCyclicReads | active_reads | threads | Number of active cyclic reads |
| Gateway cyclic reads | c8y_gatewayCyclicReads | avg_interval | ms | Average cyclic read rate overall |
| Gateway memory | c8y_gatewayMemory | max | MB | Gateway JVM max memory |
| Gateway memory | c8y_gatewayMemory | allocated | MB | Gateway JVM total allocated memory |
| Gateway memory | c8y_gatewayMemory | free | MB | Gateway JVM free memory |
| Gateway repository queues | c8y_gatewayRepositoryQueues | measurement_queue | measurements | Number of measurements currently in the queue |
| Gateway repository queues | c8y_gatewayRepositoryQueues | event_queue | events | Number of events currently in the queue |
| Gateway repository queues | c8y_gatewayRepositoryQueues | alarm_queue | alarms | Number of alarms currently in the queue |
| Server response time | c8y_serverResponseTime | response_time | ms | OPC UA server response time |
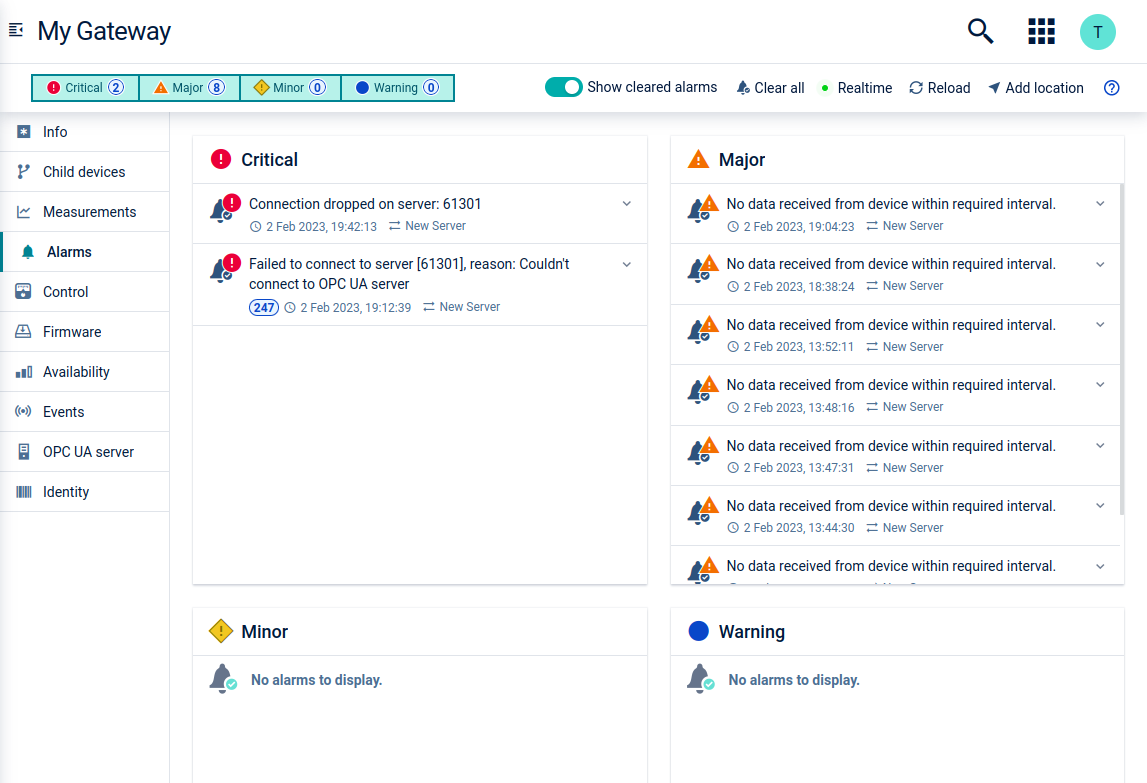
Monitoring alarms
On the gateway device, the Alarms tab shows all alarms raised either on the gateway or on the servers.
There are three alarm types which can be raised:
- Connection loss - If the gateway fails to connect to the OPC UA server a critical alarm is raised.
- Gateway crash - If the gateway crashes or is abruptly shut down a major alarm is raised.
- No data arrived within interval - If the status interval check value in the OPC UA server configuration is exceeded a major alarm is raised.
Monitoring alarm details
The following is the full list of monitoring alarms created by the gateway:
| Text | Alarm type | Severity | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| EventRepository is constantly growing! Possible memory overflow which will result in gateway crash! | c8y_ua_GatewayQueueGrowth_EventRepository | CRITICAL | |
| AlarmRepository is constantly growing! Possible memory overflow which will result in gateway crash! | c8y_ua_GatewayQueueGrowth_AlarmRepository | CRITICAL | |
| MeasurementRepository is constantly growing! Possible memory overflow which will result in gateway crash! | c8y_ua_GatewayQueueGrowth_MeasurementRepository | CRITICAL | |
| Gateway crashed on last run! Please check the log files and memory dumps to see what caused this | c8y_ua_GatewayCrash | MAJOR | This alarm is also raised when the gateway process was not terminated gracefully |
| Failed to connect to server [{serverId}], reason: {reason} | c8y_ua_ServerConnectionFailed | CRITICAL | This alarm will be cleared by the gateway when the connection to the server has been established successfully |
| Connection dropped on server: {serverId} | c8y_ua_ConnectionDropped | CRITICAL | This alarm will be cleared by the gateway when the connection has been restored |
Monitoring events
On the gateway device, the Events tab shows all events related to the gateway-server connection. Additionally, you can see when the gateway has started and when it ends.
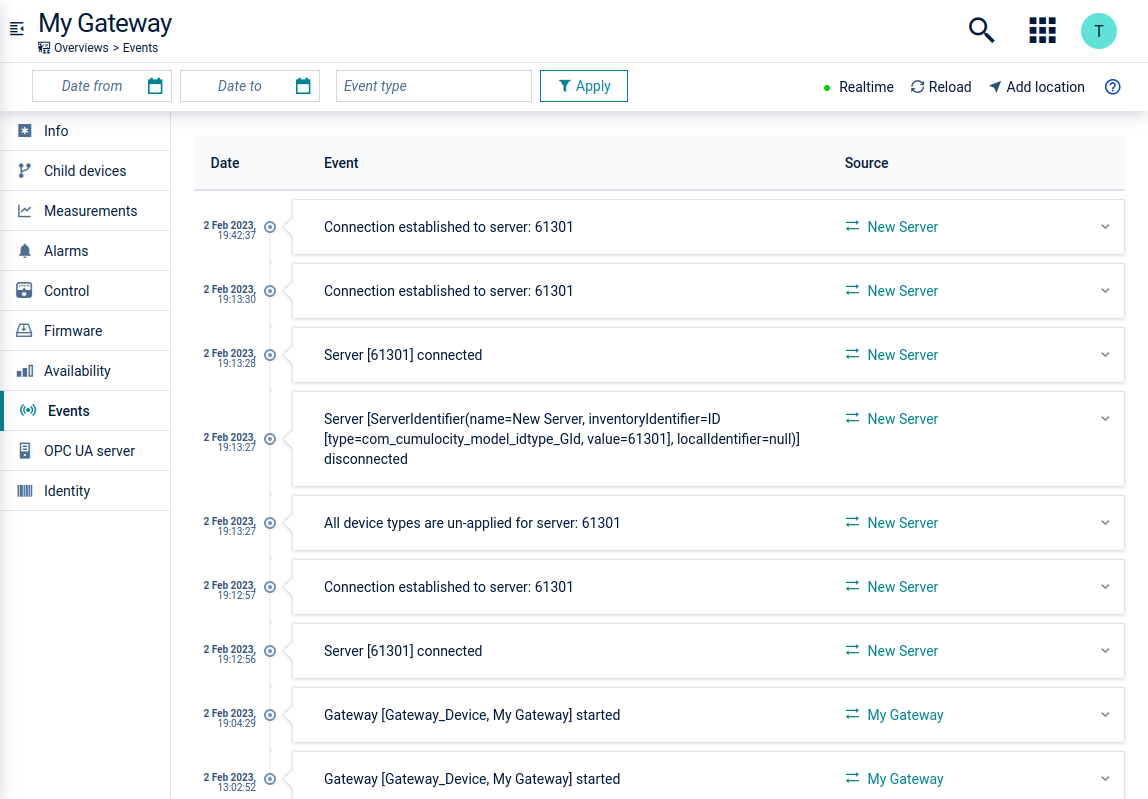
Monitoring event details
The following is the full list of monitoring events created by the gateway:
| Text | Event type | Event source | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gateway [{gateway identifier}, {gateway name}] started | c8y_ua_GatewayStarted | The gateway managed object | This event is created when the gateway has been started and authenticated with the Cumulocity IoT platform |
| Connection established to server: {server ID} | c8y_ua_ConnectionEstablished | The server managed object | This event is created when the server connection is established - either first time or a reconnection |
| Server {server ID} connected | c8y_ua_ServerConnected | The server managed object | This event is created when server is connected successfully by the Connection Manager. This event is not created if it is a reconnection. This event is normally followed by an event of type c8y_ua_ConnectionEstablished |
| Server disconnected: {server ID} | c8y_ua_ServerDisconnected | The server managed object | This event is created when the server is disconnected proactively by the Connection Manager |
Device protocols
Adding a new device protocol
-
In the Device protocols page, click New device protocol in the top menu bar and select OPC UA as device protocol type.
-
In the resulting dialog box, enter a name and an optional description for the device protocol.
-
Optionally, a reference server can be selected. Selecting a reference server allows you to create device protocols based on the OPC UA model stored on an OPC UA server. This greatly simplifies the mapping process, as device protocols can be created based on OPC UA browse paths being actually present on the server.
-
Click Create.
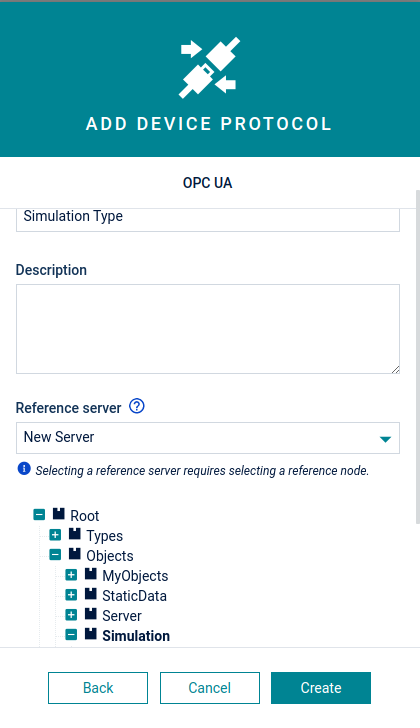
Once the device protocol is created, various configuration settings such as variables, data reporting and constraints can be applied. Initially, the device protocol will be inactive. When active, the gateway will scan the address space of all servers and will automatically apply the device protocol to all nodes which match the criteria. When the device protocol is configured, click Save.
Adding a new variable
- Click Add variable under the Variables section.
- Enter the path and the name of the variable. The path can be the exact browse path or a regular expression of the browse path. If it is a regular expression, it must be wrapped inside regex(…). For example:
regex(2:Objects)orregex(urn:test.namespace:Objects\\d). Note that the namespace index and the namespace URI are not part of the regular expression itself but they will be quoted as literal strings. When using a regular expression, keep in mind that it might be matching many nodes in the address space and resulting in unexpected incoming data. Our recommendation is to use it with great care and together with other exact browse paths in the same mapping if possible. For example,["2:Objects", "regex(2:MyDevice\\d)", "..."] - Select either the default or the custom data reporting. The default option uses the data reporting mechanism used in the device protocol. The custom option will let you configure a data reporting mechanism only for the current variable.
- Additionally, different functionalities such as sending measurements, creating alarms, sending events and custom actions for each variable can be selected.
- Click Save to save your settings.
The gateway has a scheduling job and after the variables are saved, the gateway will check whether the variables exist under the subtree of the node. Afterwards, for each node a child device of the server is created. The child devices will contain data based on the configuration of the device protocol. The node child devices will also be listed in the All devices page.
http://www.prosysopc.com/OPCUA/SimulationNodes:Counter1. A node ID equal to “ns=5;s=Simulation” will have the following namespace representation nsu=http://www.prosysopc.com/OPCUA/SimulationNodes;s=Simulation. In both examples the fifth element of the server’s namespace array has a value of http://www.prosysopc.com/OPCUA/SimulationNodes.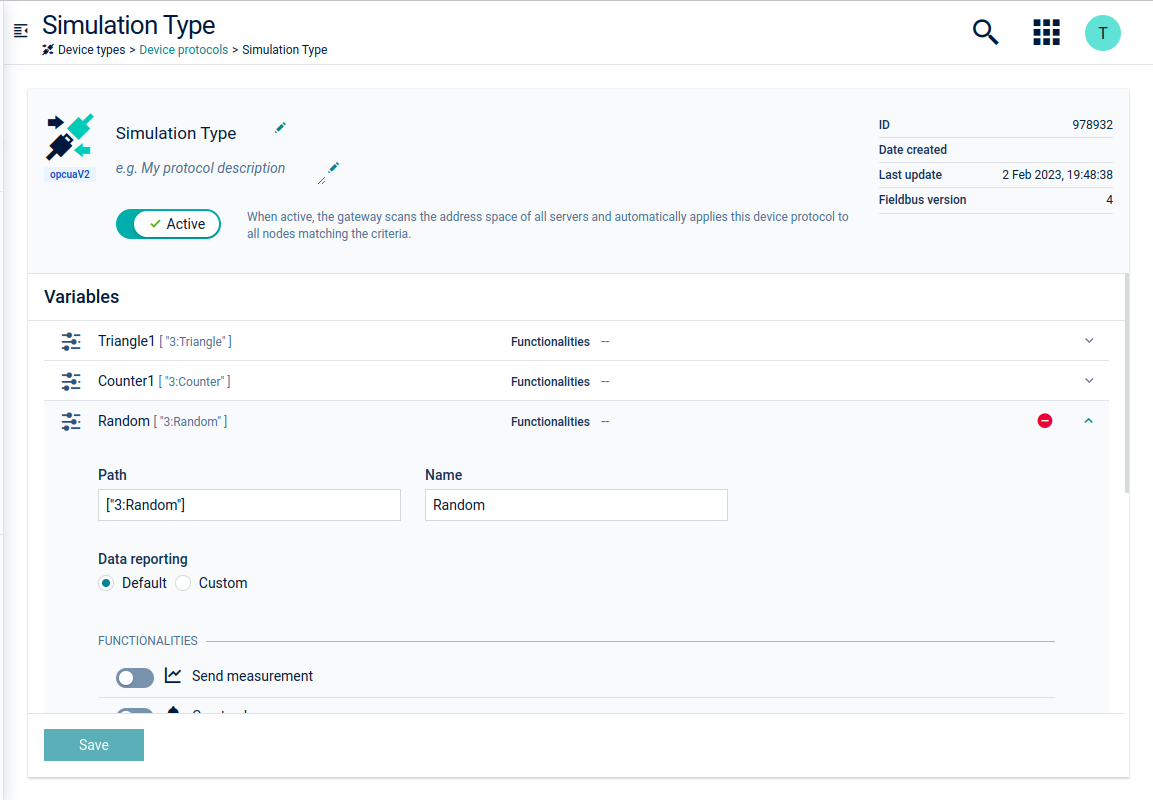
The functionalities that can be enabled are the following:
Send measurement
Turn on Send measurement to specify a measurement.
Specify the following parameters:
- Enter the type of the measurement, for example, “c8y_AccelerationMeasurement”.
- Series are any fragments in measurements that contain a “value” property, for example, “c8y_AccelerationMeasurement.acceleration”.
- Specify the unit of the given measurement, for example, “m/s” for velocity.
All measurements which exceed the Java Long ranges for Long.Max_VALUE(9,223,372,036,854,775,807) or Long.MIN_VALUE(-9,223,372,036,854,775,807) are converted internal to double values with scientific notation (for example 9.223372036854778e+24) to ensure the storage in the database. This may result in a less precise rounded value.
Create alarm
Turn on Create alarm if you want to create an alarm out of the resource.
Specify the following parameters (all mandatory):
- Severity - One of CRITICAL, MAJOR, MINOR, WARNING
- Type
- Text
Send Event
Turn on Send event to send an event each time you receive a resource value.
Specify the following parameters:
- Enter the type of the event, for example, “com_cumulocity_model_DoorSensorEvent”.
- Enter the text which will be sent, for example, “Door sensor was triggered”. You can also get the resource value populated to the event text by defining the value placeholder:
Door sensor was triggered, event value: ${value}
The value will also be populated as a fragment of the created event, under a static fragment name as the following:
{
"type": "com_cumulocity_model_DoorSensorEvent",
"text": "Door sensor was triggered",
"c8y_ua_DataValue": {
"serverTimestamp": 132403410091850000,
"sourceTimestamp": 132403410091850000,
"value": {
"value": 381632714
},
"statusCode": 0
}
}
The node values under this static fragment that are numeric and exceed the Java long ranges for Long.Max_VALUE(9,223,372,036,854,775,807) or Long.MIN_VALUE(-9,223,372,036,854,775,807) are converted internally to double values with scientific notation (for example 9.223372036854778e+24) to ensure the storage in the database. This may result in a less precise rounded value. However, the node value that is populated for the value placeholder in the event text will have the actual value even if it exceeds the long range.
Custom Actions
Custom actions are HTTP POST requests which the gateway will send to a defined custom URL. You can define custom headers and body template with the following placeholders available:
- ${value}: value of specific node
- ${serverId}: ID of OPC-UA server
- ${nodeId}: ID of source node
- ${deviceId}: ID of source device
Below there is an example of a full device protocol that configures a custom action:
{
"name": "My device protocol for HttpPost",
"referencedServerId": "{serverId}",
"referencedRootNodeId": "ns=2;s=HelloWorld/Dynamic",
"enabled": true,
"subscriptionType" : {
"type": "Subscription",
"subscriptionParameters": {
"samplingRate": 1000
}
},
"applyConstraints": {
"matchesNodeIds": [
"ns=2;s=HelloWorld/Dynamic1"
]
},
"mappings": [
{
"browsePath": [
"2:Double"
],
"customAction": {
"type": "HttpPost",
"endpoint": "http://my.endpoint.local",
"bodyTemplate": "{\"text\": \"I am coming from Http POST, value: ${value} \", \"type\": \"HttpPostMO\"}",
"headers": {
"Authorization": "Basic MYAUTHCREDENTIALS==",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
}
}
}
]
}
Monitoring events for device protocol application
When a device protocol has been applied to or un-applied from a node, a monitoring event is generated as the following:
Device type has been applied
- Event type - c8y_ua_DeviceTypeApplied
- Event text - Device type: {device type ID} is applied to root node: {root node ID} of server: {server ID}
- Event source - The server managed object

Device type has been un-applied
- Event type - c8y_ua_DeviceTypeUnapplied
- Event text -
- If the device type has been un-applied from all nodes on the server: Device type: {device type ID} is un-applied from all nodes of server: {server ID}
- If the device type has been un-applied from a specific node on the server: Device type: {device type ID} is un-applied from root node: {root node ID} of server: {server ID}
- If all device types have been un-applied for the server: All device types are un-applied for server: {server ID}
- Event source - The server managed object

Custom action retry mechanism on external server failure
If a custom action fails, a retry mechanism will be processed. This is configured in the application YAML file, and the queues will be stored in the event repository.
Queues are collections of failed custom actions, including the complete HTTP request of this custom action. Each entry of the queue is one failed custom action.
A background scheduler task will retry each queue up to the number of maxRetries. If maxRetries is reached the queue will be stored as a permanently failed queue in the event repository.
All elements of the queue are retried after the retry delay has passed. In effect, the count of the elements in the queue is decreases with each successful retried custom action.
This mechanism can be configured in the configuration section gateway.mappingExecution.http.failureHandling (see also Gateway Configuration: Additional customization) using the following properties:
Setting |
Default | Value format | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| enabled | true | boolean (true/false) | true | Activate or deactivate the fail over for custom actions |
| maxRetries | 5 | number | 5 | Number of retries for failed queues. If the maximum is reached the queue is saved as permanently failed and never tried again. Default is 5. |
| noRetryHttpCodes | empty | Comma-separated list of HTTP response codes | 400,500 | If retries are enabled (failureHandling.enabled=true), this setting allows retries to be skipped for certain HTTP response codes. In the given example requests that have received a 400 Bad Request or a 500 Internal server error response will not be retried. |
| retryDelay | 120 | number | 120 | Minimum delay in seconds between two retries of the same request. |
Data reporting
There are three data reporting mechanisms which can be applied to read all mapped browse paths:
- None - The gateway will not read values automatically. The mappings will be applied only when manual read operations are performed on mapped nodes.
- Cyclic Read - The gateway reads values from mapped nodes at specified interval rates in milliseconds. The minimum allowed rate is 50 milliseconds.
- Subscription - The gateway retrieves values by using OPC UA’s own subscription mechanism.
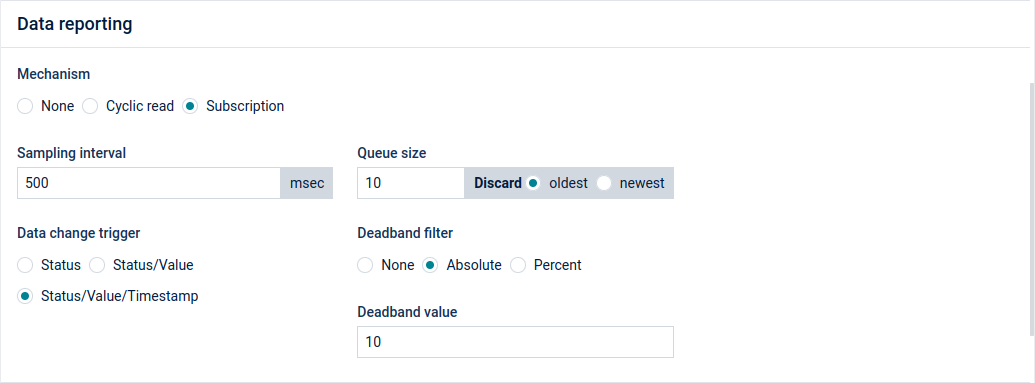
Possible parameters:
- Sampling interval (required) - Defines a time interval individually for each mapped node. This is the rate at which the server checks the data source for changes.
- Queue size - The size of the queue where it holds the samples before reporting. If you wish to record samples at a faster rate than reporting interval, you will also need to reserve a longer queue size, to be able to keep all the samples in the server. The reporting interval is defined for the gateway and the value is configurable with the YAML file (see gateway.subscription.reportingRate).
- Discard - Select whether to discard the oldest or the newest item if the samples are exceeding the queue size.
- Data change trigger:
- Status - Triggers notification if node’s status has changed.
- Status/Value - Triggers notification if node’s status or value has changed.
- Status/Value/Timestamp - Triggers notification if node’s status, value or timestamp has changed.
- Deadband filter - Deadband filter makes notified data values to be filtered.
- None - No filter will be applied. This option is selected by default.
- Absolute - Contains the absolute change in a data value which causes the generation of a notification. This parameter applies only to variables with any number data type.
- Percent - The value is defined as the percentage of the EU range. It applies only to analog items with a valid EU range property. This range is multiplied with the deadband value and is then compared to the actual value change in order to determine the need for a data change notification.
Applying constraints
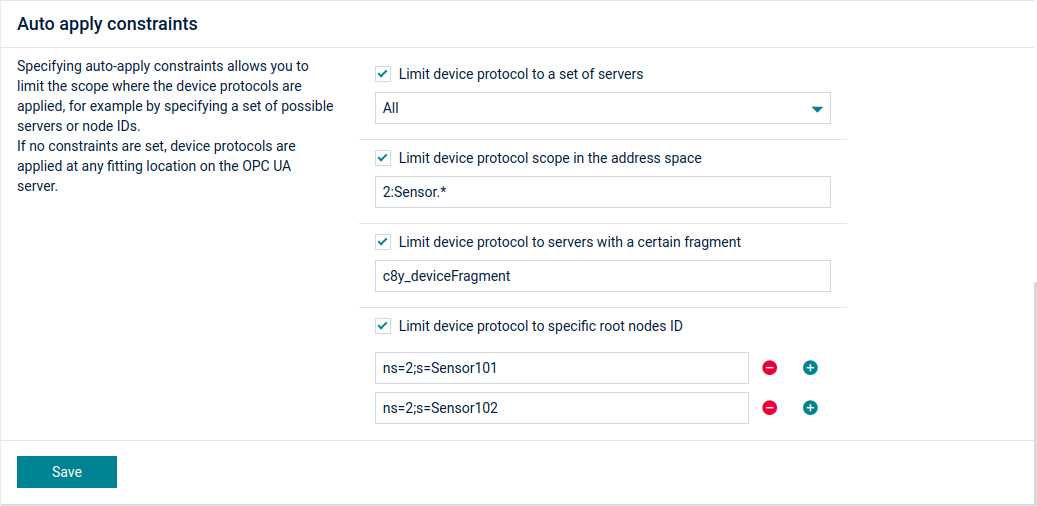
Specifying auto-apply constraints allows you to limit the scope in which the device protocols are applied, for example by specifying a set of possible servers or node IDs. If no constraints are set, device protocols are applied at any fitting location on the OPC UA server.
The following constraints can be applied:
- Limit device protocol to a set of servers - Limit the device protocols to a particular set of servers. This is useful if you want to have 1 device type for each OPC UA server. Simply click on the dropdown menu and select the desired servers.
- Limit device protocol scope in the address space - Limit the scope to servers which have the entered path in their address space.
- Limit device protocol to servers with a certain fragment - The device protocol will only be available to the servers which have the entered fragment.
- Limit device protocol to specific root nodes ID - A list of “root” node IDs (from which your browsePath is defined) to which the device protocol should be applied. For example, if there is only one server and the device protocol is applied to two node IDs, two child devices of the server will be created. Note that if the device protocol variables do not exist in the root nodes, the device protocol will not be applied to the root node server.
Bad StatusCode handling
The gateway creates an alarm with status WARNING for the corresponding OPC UA server managed object when the received DataValue of a node has an abnormal status code (such as BAD or UNCERTAIN). The alarm text in the Cumulocity IoT platform will provide the necessary information such as the node ID, and the StatusCode information (code, value, and description).
The type of the alarm is constructed as c8y_ua_DataValueAbnormal_<nodeId>_<StatusCode>_<value>. This alarm due to the abnormal status code for a node is created once,
and the counter is not incremented in the next read operations. The alarm will be cleared by the OPC UA device gateway when the status code is back to normal in the following read operations.
The full list of abnormal alarms are stored in the server managed object under the c8y_ua_DataValueAbnormalAlarms fragment.
REST APIs
While the Cumulocity IoT user interface for OPC UA provides an easy and visual way to configure and build your OPC UA solution, the OPC UA management microservice gives you the possibility to do it via RESTful web service.
The full API definitions can be found at /service/opcua-mgmt-service/swagger-ui.html.
OPC UA server resources
Connect a new OPC UA server to the gateway
Endpoint
POST /service/opcua-mgmt-service/gateways/{gatewayId}/servers
Description
Connect a new OPC UA server to the gateway or update the existing server with a new configuration.
Payload
{
"name": "My Server",
"config": {
"securityMode": "NONE",
"serverUrl": "opc.tcp://127.0.0.1:53530/OPCUA/SimulationServer",
"autoScanAddressSpace": true
}
}
Payload data structure explained:
| Field | Type | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| id | string | yes/no | String. Id of the OPC UA server in case of updating an existing server. When connecting a new server, this must not be provided. |
| name | string | yes | Server managed object name. |
| requiredInterval | integer | no | How frequently the server is expected to send data to the Cumulocity IoT platform. |
| config | ServerConnectionConfig | yes | Connection configuration to the OPC UA server. |
Data structure for ServerConnectionConfig:
| Field | Type | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| securityMode | string | yes | String enum, mandatory. Security mode for connection to OPC UA server. Possible values: NONE, BASIC128RSA15_SIGN, BASIC128RSA15_SIGN_ENCRYPT, BASIC256_SIGN, BASIC256_SIGN, BASIC256_SIGN_ENCRYPT, BASIC256SHA256_SIGN, BASIC256SHA256_SIGN_ENCRYPT. |
| serverUrl | string | yes | String, mandatory. OPC UA server URL. |
| autoScanAddressSpace | Boolean | no | Boolean. Whether the gateway should scan the address space automatically the first time it connects. Default is true. |
| rescanCron | string | no | String. Regular expression that defines how the address space rescanning should be scheduled. If this is not set, no auto-rescan will be triggered. |
| autoReconnect | Boolean | no | Boolean. Whether the gateway should try to reconnect to the OPC UA server once the connection drop is detected. Default is true. |
| timeout | integer | no | Integer. Define the default communication timeout that is used for each synchronous service call. This value is set to each service request and the OPC UA gateway will wait for the response message for that long. |
| statusCheckInterval | integer | no | Integer. Define the status check interval, that is, how often the server status is read. Default is 3 (seconds). |
| maxResponseMessageSize | long | no | Integer. Define the maximum size, in bytes, for the body of any response message from the server. Default is 50.000.000 (50 MB). To make it unlimited, set this to 0. |
| targetConnectionState | string | no | String enum. Possibe values: enabled/disabled. Whether the connection the the target OPC UA server is enabled. |
| userIdentityMode | string | no | User identity. Possible values: Anonymous, UserName, Certificate, IssuedToken. Default is Anonymous. |
| userName | string | yes/no | Authentication username when user identity mode is UserName. |
| userPassword | string | no | Authentication password when user identity mode is UserName. Set the value in order to change the authentication password. If it is not set, the previously stored authentication password is preserved. |
| keystoreBinaryId | string | yes/no | If the user identity mode is Certificate, this is the binary object ID of the uploaded keystore. |
| keystorePass | string | no | If the user identity mode is Certificate, this is the password of the uploaded keystore. |
| certificatePass | string | no | If the user identity mode is Certificate, this is the password of the private key embedded in the keystore. |
| cyclicReadBulkSize | integer | no | For cyclic reads, this defines how many nodes can be read at once from the OPC UA server. This is applicable only for nodes resulting from the application with the same device type, matching root node and sharing the same reading parameters (rate and max age). Default is 1000 as defined in the application YAML file. |
| alarmSeverityMappings | map<string, string> | no | Alarm severity mappings from the OPC UA event severity to the Cumulocity IoT alarm severity. This is applicable only for UAAlarmCreation. The key of this map is the lower bound value of the OPC UA event severity in the range. The value of this map is the expected severity of the alarm being created. For example, to map the OPC UA severity of the range 200-400 to a MINOR Cumulocity IoT alarm, put this entry to the map: "200": "MINOR".If this is given, it will override the alarm severity mappings that are specified in the configuration YAML file. Note that, if the severity field for alarm mapping is provided, this alarmSeverityMappings will have no effect. Example: "201": "WARNING","401": "MINOR","601": "MAJOR","801": "CRITICAL"
Additionally, the Severity attribute should be added in the subscribed attributes (uaEventMappings -> attributes) in the device type in order to get the severity value of the OPC UA event. |
| alarmStatusMappings | map<string, string> | no | The status of an alarm in Cumulocity IoT is defined by multiple conditions on OPC UA servers. For example, if the value of AcknowledgedState node is "Acked" and ConfirmedState is "Confirmed",
then the status of the alarm in Cumulocity IoT is expected as ACKNOWLEDGED. They might vary with different servers as well. This field enables the user to configure the desired conditions (based on the information retrieved
from the event type nodes of the OPC UA server) while creating alarms via UA event mappings (this is not applicable for OPC UA data value alarm creation).
The example below shows that the keys of the map are the user-defined expressions and the value represents their corresponding desired status of the alarm. The variables that can be used in the expressions are the selected
attributes provided in the subscription definition of the device type. It can be written down either by using the relevant node names
(for example EnabledState.text == 'Enabled'), or the qualified browse name with namespace index (for example ['0:EnabledState'].text == 'Enabled').
If the variables are not provided in the subscribed attributes (uaEventMappings -> attributes), they are considered null.
If the alarm status is explicitly provided in the alarm mapping (uaEventMappings -> alarmCreation) of the device type, these alarm status mappings have no effect.
The Spring Expression Language(SpEL) has been used to parse these conditions, but only Boolean expressions are allowed.
See the alarmStatusMappings example below the table. Info
There are three alarm statuses in Cumulocity IoT, namely ACTIVE, ACKNOWLEDGED, and CLEARED. If the user-defined conditions overlap and as a result more than one alarm status is realized during the alarm creation, then the status is selected based on priority. ACTIVE has the highest priority, followed by ACKNOWLEDGED and then CLEARED status with the least priority. If the expression could not be evaluated then the gateway logs a warning and the alarm status is assumed as ACTIVE. The alarm status is also assumed as ACTIVE, if the default status is not specified, and the parameters do not match any other defined condition.
|
| subscribeModelChangeEvent | Boolean | no | The subscription to model change event can be enabled/disabled using this property. Default value is "false" (disabled), which means any change in the address space nodes of the OPC UA server in runtime will not automatically be updated in the address space of Cumulocity IoT. This property must be explicitly set to "true" to detect and persist the address space changes on runtime. |
alarmStatusMappings example
{
"alarmStatusMappings": {
"['0:ActiveState'].text == 'Active' and ['0:AckedState'].text != 'Acknowledged'": "ACTIVE",
"['0:ActiveState'].text == 'Active' and ['0:AckedState'].text == 'Acknowledged'": "ACKNOWLEDGED",
"['0:ActiveState'].text == 'Inactive'": "CLEARED",
"default": "ACTIVE"
}
}
Alarms status changed by OPC UA server
If events operated on the OPC UA server change their status, these changes can be reflected as internal alarms.
To catch these events and convert them into internal alarms, a UA event mapping with the alarmCreation definition in device protocol and alarmStatusMappings in server configuration are required.
For better performance an in-memory map is used to store the alarm type and the internal representation. These values are also stored on the filesystem and survive a possible crash or restart of the gateway. When the alarm is cleared then its entry is removed from the in-memory map.
The size of the map can be adjusted by several parameters in the configuration file.
With maxEntries you can specify the expected number of alarms at the same time, and it is hard-connected with the maxBloatFactor.
This factor lets you define a possible maximum of maxEntries to be extended. For example, a default maxEntries value of “100000” and ‘maxBloatFactor’ set to “5.0” results in a maximum of 500000 entries.
The avarageKeySize defines the used key size resulting from the length of the type and the external ID.
It’s used to calculate the local file size bound to the entry size.
# To avoid many REST calls to the inventory an in-memory map with a crash backup functionality is included.
alarmStatusStore:
# Expected number of maximum alarms at the same time
maxEntries: 100000
# The average size of the keys on the map. Needed for calculation of the size of the database file.
averageKeySize: 30
# The number of maxEntries multiplied with this factor results in the real max size of the database file. Resize is done only if needed.
maxBloatFactor: 5.0
Get all servers of a gateway device
Method
GET /service/opcua-mgmt-service/gateways/{gatewayId}/servers
Parameters
| Field | Field type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| gatewayId | Path variable | Managed object ID of the gateway that should connect to the OPC UA server. |
Example response
[
{
"id": "25197",
"gatewayId": "800",
"name": "My OPC UA server",
"requiredInterval": 1,
"config": {
"securityMode": "NONE",
"serverUrl": "opc.tcp://127.0.0.1:12686/CumulocityOPCUAServer",
"userIdentityMode": "Anonymous",
"timeout": 30,
"autoReconnect": true,
"statusCheckInterval": 40,
"targetConnectionState": "enabled"
},
"namespaceTable": [
"http://opcfoundation.org/UA/",
"urn:cumulocity:opcua:test:server:ee8ff646-cc83-4a1f-ad29-97356c496ef0",
"urn:cumulocity:opcua:test:server"
],
"c8y_Availability": {
"lastMessage": "2020-08-27T12:43:22.585+0000",
"status": "UNAVAILABLE"
},
"c8y_Connection": {
"status": "DISCONNECTED"
},
"c8y_RequiredAvailability": {
"responseInterval": 1
}
}
]
Delete and disconnect an OPC UA server
Endpoint
DELETE /service/opcua-mgmt-service/servers/{serverId}
Description
Delete the OPC UA server managed object. Once the DELETE request is received by the OPC UA management service, the specified server along with all its address space nodes created in the Cumulocity IoT platform will be deleted. The service will retain all the child devices of the server, and their corresponding data, which were created by the device protocols.
Parameters
| Field | Field type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| serverId | Path variable | Managed object ID of the OPC UA server. |
Response
200 OK
Address space resources
Get an address space node by ID
Endpoint
GET /service/opcua-mgmt-service/servers/{serverId}/address-spaces/get
Description
Get a node in the server address space specified by the given node ID. The node ID must be URL encoded.
Parameters
| Parameter | Parameter Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| serverId | Path variable | Integer, mandatory. OPC UA server managed object ID. |
| nodeId | Query param | Mandatory. Node ID of the node to get. |
| withUri | Query param | Boolean, default is false. Whether the result should use address space URI instead of index. |
Example
Endpoint: GET /service/opcua-mgmt-service/servers/10/address-spaces/get?nodeId=i%3D84
{
"nodeId": "i=84",
"nodeClass": 1,
"nodeClassName": "Object",
"browseName": "0:Root",
"browsePath": null,
"displayName": "Root",
"description": "The root of the server address space.",
"references": [
{
"referenceId": "i=35",
"targetId": "i=87",
"referenceLabel": "Organizes",
"targetLabel": "Views",
"targetBrowseName": "Views",
"inverse": false,
"hierarchical": true
},
{
"referenceId": "i=40",
"targetId": "i=61",
"referenceLabel": "HasTypeDefinition",
"targetLabel": "FolderType",
"targetBrowseName": "FolderType",
"inverse": false,
"hierarchical": false
}
],
"attributes": {
"eventNotifier": 0
},
"absolutePaths": [
[
"0:Root"
]
],
"ancestorNodeIds": [
[]
]
}
Get children of a given node
Endpoint
GET /service/opcua-mgmt-service/servers/{serverId}/address-spaces/children
Description
Get all child nodes of the given node specified by the node ID in the server address space. The node ID must be properly URL encoded.
Parameters
| Parameter | Parameter Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| serverId | Path variable | Integer, mandatory. OPC UA server managed object ID. |
| nodeId | Query param | Mandatory. Node ID of the node to get. |
| withUri | Query param | Boolean, default is false. Whether the result should use address space URI instead of index. |
Example
Endpoint: GET /service/opcua-mgmt-service/servers/10/address-spaces/children?nodeId=i%3D84
[
{
"nodeId": "i=86",
"nodeClass": 1,
"nodeClassName": "Object",
"browseName": "0:Types",
"browsePath": null,
"displayName": "Types",
"description": "The browse entry point when looking for types in the server address space.",
"references": [
{
"referenceId": "i=40",
"targetId": "i=61",
"referenceLabel": "HasTypeDefinition",
"targetLabel": "FolderType",
"targetBrowseName": "FolderType",
"inverse": false,
"hierarchical": false
},
{
"referenceId": "i=35",
"targetId": "i=86",
"referenceLabel": "OrganizedBy",
"targetLabel": "Types",
"targetBrowseName": "Types",
"inverse": true,
"hierarchical": true
}
],
"attributes": {
"eventNotifier": 0
},
"absolutePaths": [
[
"0:Root",
"0:Types"
]
],
"ancestorNodeIds": [
[
"i=84"
]
]
}
]
Browse a node
Endpoint
GET /service/opcua-mgmt-service/servers/{serverId}/address-spaces/browse
Description
Browse a node from a base node following the given browse path. This basically searches for a node with relative browse path to the other node.
Parameters
| Parameter | Parameter Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| serverId | Path variable | Integer, mandatory. OPC UA server managed object ID. |
| nodeId | Query param | Node ID of the node to browse from. Default is root node (i=84). |
| browsePath | Query param | Mandatory. Browse path to browse from the give node. Browse path can be a single param or an array to represent a path from the given node to the target node. To specify the browsePath as an array, repeat the browsePath query. Example: .../browse?browsePath=L1&browsePath=L2. |
| withUri | Query param | Boolean, default is false. Whether the result should use address space URI instead of index. |
Example
Endpoint: GET /service/opcua-mgmt-service/servers/10/address-spaces/browse?nodeId=i%3D84&browsePath=Objects
[
{
"nodeId": "i=85",
"nodeClass": 1,
"nodeClassName": "Object",
"browseName": "0:Objects",
"browsePath": null,
"displayName": "Objects",
"description": "The browse entry point when looking for objects in the server address space.",
"references": [
{
"referenceId": "i=35",
"targetId": "i=2253",
"referenceLabel": "Organizes",
"targetLabel": "Server",
"targetBrowseName": "Server",
"inverse": false,
"hierarchical": true
},
{
"referenceId": "i=35",
"targetId": "ns=2;s=Cumulocity",
"referenceLabel": "Organizes",
"targetLabel": "Cumulocity",
"targetBrowseName": "2:Cumulocity",
"inverse": false,
"hierarchical": true
}
],
"attributes": {
"eventNotifier": 0
},
"absolutePaths": [
[
"0:Root",
"0:Objects"
]
],
"ancestorNodeIds": [
[
"i=84"
]
]
}
]
Device type resources
These resources provide the APIs for manipulating device types.
Creating a new device type
Endpoint
POST /service/opcua-mgmt-service/device-types
Sample payloads
-
Measurement mappings using subscription
{ "name": "My device type", "enabled": true, "mappings": [ { "browsePath": [ "2:Dynamic", "2:Double" ], "measurementCreation": { "unit": "T", "type": "MyMeasurementType", "fragmentName": "MyMeasurement", "series": "MySeries" } } ], "subscriptionType": { "type": "Subscription", "subscriptionParameters": { "samplingRate": 5000 } } }
-
Event mappings using cyclic read
{ "name": "My device type", "enabled": true, "mappings": [ { "browsePath": [ "2:Dynamic", "2:Integer" ], "eventCreation": { "type": "MyEventType", "text": "My event with value ${value}" } } ], "subscriptionType": { "type": "Cyclicread", "rate": 5000 } } -
Alarm mappings using subscription
{ "name": "My device type", "enabled": true, "mappings": [ { "browsePath": [ "2:Dynamic", "2:Boolean" ], "alarmCreation": { "type": "MyAlarm", "severity": "MAJOR", "text": "Heads up, the level is high!" } } ], "subscriptionType": { "type": "Subscription", "subscriptionParameters": { "samplingRate": 5000 } } } -
UA events mappings into alarm and event
{ "name": "My device type", "enabled": true, "uaEventMappings": [ { "browsePath": [ "Server" ], "eventTypeId": "i=2041", "attributes": [ "Message", "Severity" ], "alarmCreation": { "text": "ALARM! message: ${0}", "severity": "MAJOR", "status": "ACTIVE", "type": "c8y_myEvent_alarm_${1}" } } ] }
Full payload data structure explained:
| Field | Type | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| name | string | yes | Device type name. |
| enabled | Boolean | no | Whether the device type is enabled and should be applied to the connected servers or not. Default is false. |
| description | string | no | |
| mappings | array<Mapping> | no | Define the mappings from OPC UA data into Cumulocity IoT measurements, events and alarms. |
| uaMappings | array<UAMapping> | no | Define the mappings from OPC UA alarms and events into Cumulocity IoT alarms and events. |
| referencedNamespaceTable | array |
no | Reference namespace table if known. This is then used to convert the browse paths with namespace index into namespace URL. This is to make sure that the mappings are still the same even when the namespace index gets changed. |
| subscriptionType | SubscriptionType | no | Define the mechanism how to collect data from the OPC UA servers. There are two mechanisms that can be used: Cyclic read and subscription. This is not mandatory however if the device type is enabled and no subscription type is specified, the device will not be applied to any node. |
| processingMode | string | no | Define the Cumulocity IoT processing mode for incoming data. Refer to HTTP usage > Process mode in the Cumulocity IoT OpenAPI Specification for more information. Possible values: PERSISTENT, TRANSIENT, QUIESCENT, CEP. Default is PERSISTENT. Note that for the alarm mappings, only the PERSISTENT mode is supported regardless what is being given here. |
| overiddenSubscriptions | OverriddenSubscription | no | While the subscriptionType defines how data can be collected from the OPC UA server, this option allows you to override the mechanism for particular browse paths. For example you can have a subscription applied globally with a sampling rate of 1000ms but you can apply sampling rate of 500ms for particular browse paths. |
| applyConstraints | ApplyConstraint | no | Limit the places in the address space where the device type should be applied. |
Data structure for Mapping
| Field | Type | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| name | string | no | |
| browsePath | array |
yes | The browse path. The path can be the exact browse path or a regular expression of the browse path. If it is a regular expression, it must be wrapped inside *regex(...)*. For example: `regex(2:Objects)` or `regex(urn:test.namespace:Objects\\d)`. Note that the namespace index and the namespace URI are not part of the regular expression itself but they will be quoted as literal strings. When using a regular expression, keep in mind that it might be matching many nodes in the address space and resulting in unexpected incoming data. Our recommendation is to use it with great care and together with other exact browse paths in the same mapping if possible. For example, `["2:Objects", "regex(2:MyDevice\\d)", "..."]` |
| measurementCreation | MeasurementCreation | no | Mappings for measurement. |
| eventCreation | EventCreation | no | Mappings for event. |
| alarmCreation | AlarmCreation | no | Mappings for alarm. If the value of the mapped resource is "true" (in case of Boolean), or a positive number (in case of integer/double), then the alarms are created in ACTIVE state. The alarm de-duplication prevents the creation of multiple alarms with the same source and type, thereby only incrementing the count of the existing alarm. The alarms will be CLEARED as soon as the value is changed to "false", or a number that is less than or equals to 0. |
| customAction | HttpPostAction | no | Mappings for custom action. Only HTTP POST is supported so far. |
Data structure for UAMapping
| Field | Type | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| browsePath | array |
yes | The browse path. |
| eventTypeId | string | yes | The event type ID. |
| attributes | array | yes | Selectable event attributes. The nodeId of the event source is added by default as the last selected attribute by the OPC UA device gateway. If alarmSeverityMappings are defined, also the Severity attribute needs to be added to the attributes. If alarmStatusMappings are defined, also the variables used in the expression needs to be added to the attributes. |
| eventCreation | UAEventCreation | no | Mappings for event. |
| alarmCreation | UAAlarmCreation | no | Mappings for alarm. |
Data structure for SubscriptionType
| Field | Type | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| type | string | yes | Subscription type. Possible values: Subscription, CyclicRead, None. |
| subscriptionParameters | SubscriptionParameter | yes/no | In case the subscription type is Subscription, this is required. This defines the OPC UA subscription configuration, such as sampling rate, queue size, and more. |
| cyclicReadParameters | CyclicReadParameter | yes/no | In case the subscription type is CyclicRead, this is required. This defines the cyclic read configuration, such as rate. |
Data structure for OverriddenSubscription
| Field | Type | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| browsePath | array |
yes | The browse path. |
| subscriptionType | SubscriptionType | yes | The custom subscription type that overrides the global one. |
Data structure for ApplyConstraints
| Field | Type | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| matchesServerIds | array |
no | Limit the servers by server managed object ID where the device type should be applied. |
| serverObjectHasFragment | string | no | Limit the servers by their custom fragment where the device type should be applied. |
| matchesNodeIds | array |
no | Limit the nodes in the server address space where the device type should be applied. |
| browsePathMatchesRegex | string | no | Regular expression of the browse paths where the device type should be applied. |
| serverHasNodeWithValues | ServerNodeValues | no | Limit the servers which have particular nodes with given values. |
Data structure for MeasurementCreation
| Field | Type | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| type | string | yes | Measurement type. |
| series | string | no | Measurement series. If this is omitted, it will be automatically generated by the gateway. |
| unit | string | yes | Measurement unit. |
| fragmentName | string | no | Measurement fragment name. If this is omitted, it will be automatically generated by the gateway. |
| staticFragments | array |
no | Static fragments that should be populated to the measurement. |
| overriddenProcessingMode | string | no | Custom processing mode applied to the measurement to be created. Possible values: PERSISTENT, TRANSIENT, QUIESCENT, CEP. Default: PERSISTENT. |
Data structure for EventCreation
| Field | Type | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| type | string | yes | Event type. |
| text | string | yes | Event text. This event text can be parameterized by the value of the subscribed node by using the placeholder: ${value}. |
| staticFragments | array |
no | Static fragments that should be populated to the measurement. |
| overriddenProcessingMode | string | no | Custom processing mode applied to the event to be created. Possible values: PERSISTENT, TRANSIENT, QUIESCENT, CEP. Default: PERSISTENT. |
Data structure for AlarmCreation
| Field | Type | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| type | string | yes | Alarm type. |
| text | string | yes | Alarm text. |
| severity | string | yes | Alarm severity. Possible values: WARNING, MINOR, MAJOR, CRITICAL. |
| staticFragments | array |
no | Static fragments that should be populated to the alarm. |
| overriddenProcessingMode | string | no | Custom processing mode applied to the alarm to be created. Possible values: PERSISTENT. |
Data structure for HttpPostAction
| Field | Type | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| endpoint | string | yes | Endpoint of the HTTP POST request. |
| headers | map<string, string> | no | HTTP headers of the HTTP request. |
| bodyTemplate | string | yes | Template of the request body. This can be parameterized by the following placeholders:${value}: Data value of the OPC UA node. ${serverId}: OPC UA server managed object ID.${nodeId}: ID of the node where the data is coming from.${deviceId}: Managed object ID of the source manage object. |
| retryEnabled | Boolean | no | Whether a failed HTTP POST should be retried or not. This overrides the configuration in the gateway. If this is not provided, the configuration in the gateway will be taken. |
| noRetryHttpCodes | array<integer> | no | Array of HTTP POST status exceptions by which the failed HTTP POST should not be retried if enabled. Example: [400, 500]. Note that, if this is null or missing, the exceptions will be taken from the gateway configuration. If this is provided, even with an empty array, the configuration in the gateway is disregarded. |
Data structure for UAEventCreation
This has exactly the same fields as EventCreation, however the text and type field can be parameterized with different parameters.
| Field | Type | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| text | string | yes | Event text. This event text can be parameterized by the data value of selected attributes. Put ${i} to parameterize it by the data value of attribute at index i. The index starts from 0, so put ${0} to take the first attribute, ${1} to select second attribute, and so on. |
| type | string | yes | Event type. This event type can be parameterized by the data value of selected attributes. Put ${i} to parameterize it by the data value of attribute at index i. The index starts from 0, so put ${0} to take the first attribute, ${1} to select second attribute, and so on. |
Data structure for UAAlarmCreation
| Field | Type | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| text | string | yes | Alarm text. This alarm text can be parameterized by the data value of selected attributes. Put ${i} to parameterize it by the data value of attribute at index i. The index starts from 0, so put ${0} to take the first attribute, ${1} to select second attribute, and so on. |
| type | string | yes | Alarm type. This alarm type can be parameterized by the data value of selected attributes. Put ${i} to parameterize it by the data value of attribute at index i. The index starts from 0, so put ${0} to take the first attribute, ${1} to select second attribute, and so on. |
| severity | string | no | For UAAlarmCreation, the severity is optional. If this is not provided, the severity of the alarm will be mapped using the severity mappings specified in the default gateway configuration YAML file or in the server configuration. |
| status | string | no | Alarm status. The possible values are ACTIVE, ACKNOWLEDGED, CLEARED. If this is given, the alarmStatusMappings setting in ServerConnectionConfig is ignored. |
Data structure for SubscriptionParameter
| Field | Type | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| samplingRate | integer | yes | Subscription sampling rate in milliseconds. Minimum allowed value is 50. |
| deadbandType | string | no | Possible values: Percent, Absolute. |
| deadbandValue | double | no | If the deadbandType is Percent, this ranges from 0 to 100. If the deadbandType is Absolute, this can be any double value. |
| queueSize | integer | no | Subscription queue size. |
| dataChangeTrigger | string | no | Default value is StatusValue. Possible values: Status, StatusValue, StatusValueTimestamp. |
| discardOldest | Boolean | no | Default is true. When this is true and the reported data is exceeding the queue size, the oldest elements in the queue will be discarded. If this is false, the newer elements will be discarded. |
| ranges | string | no | When the subcribed node is array type, you can provide the data range you want to get. For example: "0:3" to get elements from index 0 to 3 from the array. |
Data structure for CyclicParameter
| Field | Type | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| rate | integer | yes | Cyclic read rate in milliseconds. Minimum allowed value is 50. |
Data structure for ServerNodeValues
| Field | Type | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| matchAll | array |
no | A collection of conditions and they must all be matched. |
| matchOneOf | array |
no | A collection of conditions and at least one of them must be matched. |
Data structure for MatchingNode
| Field | Type | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| nodeId | string | yes | The node ID to match against. |
| valueMatchesOneOf | array |
no | A collection of possible values of the node, in string representation. If this is omitted, the gateway only checks for the existence of the node by given node ID. |
Get all OPC UA device types
Endpoint
GET /service/opcua-mgmt-service/device-types
Payload
The endpoint returns a JSON array of all OPC UA device types.
Get a single device type
Endpoint
GET /service/opcua-mgmt-service/device-types/{deviceTypeId}
Payload
A JSON representation of the device type with the given ID if it exists. If not, an error message is returned.
Response codes
200 OK
404 Not found
Updating a device type
Endpoint
PUT /service/opcua-mgmt-service/device-types/{deviceTypeId}
Payload
The payload of updating a device type is exactly the same as the payload of creating it. Please note that partial update is not supported. All information must be provided in the update request and will completely override the existing device type.
Deleting a device type
Endpoint
DELETE /service/opcua-mgmt-service/device-types/{deviceTypeId}
Success response
204 No Content
Operations
Cumulocity IoT operations is the interface that is used to tell the gateway what to do and how to do it. This section describes all operations that are currently supported by the gateway.
Scanning the address space
This operation triggers importing address space for a specific OPC-UA server. The server’s ID is passed as a device ID. The gateway will scan the entire address space of the server and persist a twinned representation of the address space in the Cumulocity IoT platform.
POST /devicecontrol/operations/
{
"deviceId": "<server-device-Id>",
"c8y_ua_command_ScanAddressSpace": {
"skipSync": false
},
"description": "Import address space from root node"
}
The twinned address space information is persisted in the Cumulocity IoT inventory. It is internally used to support address space browsing and to define device protocols. Hence this operation is always triggered if a new server is added to the platform.
Once the device gateway knows the address space, it uses it to handle different logics, for example applying device protocols to nodes. So if you already have the address space scanned once and stored in Cumulocity IoT, you might want the device gateway to learn one more time about server’s address space without synchronizing data into Cumulocity IoT. To achieve that, provide "skipSync": true.
When you would like to scan partial address space, you can provide the nodeId property which is used as a start node for the scan operation.
The subaddress space starting from this node as well as the ancestor nodes will be persisted in the Cumulocity IoT inventory (unless "skipSync": true is provided) as well as in the local address space file of the gateway.
POST /devicecontrol/operations/
{
"deviceId": "<server-device-Id>",
"c8y_ua_command_ScanAddressSpace": {
"nodeId":"ns=2;s=MyDevice"
},
"description": "Import address space from MyDevice node"
}
Available arguments for c8y_ua_command_ScanAddressSpace:
| Field | Type | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| nodeId | string | no | Scan of the address space starts from this node. If not provided, full scan is done starting from the root node. |
| skipSync | Boolean | no | If set to true, the address space nodes will not be synchronized to Cumulocity IoT Inventory API. Default is false. |
Reading the value of a node/nodes
This operation reads the value attribute of specific node or list of nodes.
POST /devicecontrol/operations/
{
"deviceId" : "<server-device-Id>",
"c8y_ua_command_ReadValue": {
"nodes": ["NODE_ID"],
"timestampsToReturn": "Neither"
},
"description":"read value"
}
Available arguments for c8y_ua_command_ReadValue:
| Field | Type | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| nodes | string array | yes | Array of IDs of the nodes to execute the operation |
| ranges | string | no | The index ranges of a subset of the multi-dimension array from the read attribute. The syntax is according to the OPC UA specification and will be transformed to NumericRange.
Example values to define the range for a 1D array is “0:1”, for a 2D array is “0:1,0:1” |
| maxAge | double | no | The maximum age used for the read. If the server does not have a value that is within the maximum age, it shall attempt to read a new value from the data source. If maxAge is set to 0, the server shall attempt to read a new value from the data source. Default is 0. |
| timestampsToReturn | string | no | Time stamps to return for the read attributes in the operation result. Available options are "Source", "Server", "Both", "Neither". Default is "Both". |
| expirationTime | dateTime | no | Expiration time to execute the operation. The operation is executed if it is before the given expiration time. Otherwise, the operation will fail. In this case, "Operation expired" is returned as failure reason. |
The result of this operation will contain output in the following format:
{
"results": {
"ns=2;s=MyLevel": {
"13": {
"value": {
"value": 77.0
},
"statusCode": 0,
"sourcePicoseconds": 0,
"serverPicoseconds": 0
}
}
}
}
Reading all attributes of a node
This operation returns all attributes of specific node.
{
"deviceId": "<server-device-Id>",
"c8y_ua_command_ReadNodeAttributes": {
"node": "ns=2;s=MyEnumObject"
},
"description": "Read node attributes"
}
Available arguments for c8y_ua_command_ReadNodeAttributes:
| Field | Type | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| node | string | yes | ID of the node to execute the operation |
| expirationTime | dateTime | no | Expiration time to execute the operation. The operation is executed if it is before the given expiration time. Otherwise, the operation will fail. In this case, "Operation expired" is returned as failure reason. |
The result may differ depending on the node type.
{
"Value": {
"value": 1
},
"DataType": "ns=2;s=MyEnumType",
"ValueRank": -1,
"AccessLevel": 3,
"UserAccessLevel": 3,
"MinimumSamplingInterval": -1.0,
"Historizing": false,
"DisplayName": "MyEnumObject",
"WriteMask": 0,
"UserWriteMask": 0
}
Reading an attribute
This operation supports to read one or more attributes of one or more nodes. This includes support of the range parameter to read a single element or a range of elements when the attribute value is an array.
{
"deviceId": "<server-device-Id>",
"c8y_ua_command_ReadAttribute": {
"nodes": ["ns=3;s=FloatArray"],
"attribute":"13"
},
"description": "Read attribute from ns=3;s=FloatArray"
}
Available arguments for c8y_ua_command_ReadAttribute:
| Field | Type | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| nodes | string array | yes | Array of IDs of the nodes to execute the operation |
| attribute | string | yes | The ID of the attribute according to the OPC UA specification |
| ranges | string | no | The index ranges of a subset of the multi-dimension array from the read attribute. The syntax is according to the OPC UA specification and will be transformed to NumericRange.
Example values to define the range for a 1D array is “0:1”, for a 2D array is “0:1,0:1” |
| maxAge | double | no | The maximum age used for the read. If the server does not have a value that is within the maximum age, it shall attempt to read a new value from the data source. If maxAge is set to 0, the server shall attempt to read a new value from the data source. Default is 0. |
| timestampsToReturn | string | no | Time stamps to return for the read attributes in the operation result. Available options are "Source", "Server", "Both", "Neither". Default is "Both". |
| expirationTime | dateTime | no | Expiration time to execute the operation. The operation is executed if it is before the given expiration time. Otherwise, the operation will fail. In this case, "Operation expired" is returned as failure reason. |
The result may differ depending on the node type.
{
"results": {
"ns=3;s=FloatArray": {
"13": {
"value": {
"value": [1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0, 5.0]
},
"statusCode": 0,
"sourceTimestamp": 1566572540173,
"sourcePicoseconds": 0,
"serverTimestamp": 1566573849897,
"serverPicoseconds": 0
}
}
}
}
Example operation with ranges fragment:
{
"description": "Read attribute from ns=3;s=FloatArray",
"deviceId": "<server-device-Id>",
"c8y_ua_command_ReadAttribute": {
"nodes": ["ns=3;s=FloatArray"],
"attribute":"13",
"ranges":"0:1"
}
}
The result may differ depending on the node type.
{
"results": {
"ns=3;s=FloatArray": {
"13": {
"value": {
"value": [1.0, 2.0]
},
"statusCode": 0,
"sourceTimestamp": 1566572540173,
"sourcePicoseconds": 0,
"serverTimestamp": 1566574513935,
"serverPicoseconds": 0
}
}
}
}
Read complex
This operation reads many attributes from many nodes at single call.
{
"deviceId" : "<server-device-Id>",
"c8y_ua_command_ReadComplex": {
"nodeAttrs": {
"ns=2;s=MyEnumObject": {
"13":"",
"11":""
}
}
},
"description":"Read complex"
}
Available arguments for c8y_ua_command_ReadComplex:
| Field | Type | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| nodeAttrs | map<string, map<string, string>> | yes | Map with ID of the node and inner map with ID of the attribute and the index range.
The index ranges defines a subset of the multi-dimension array from the read attribute.
The syntax is according to the OPC UA specification and will be transformed to NumericRange.
Example values to define the range for a 1D array is “0:1”, for a 2D array is “0:1,0:1”. Empty string ("") can be given to not define any range. |
| maxAge | double | no | The maximum age used for the read. If the server does not have a value that is within the maximum age, it shall attempt to read a new value from the data source. If maxAge is set to 0, the server shall attempt to read a new value from the data source. Default is 0. |
| timestampsToReturn | string | no | Time stamps to return for the read attributes in the operation result. Available options are "Source", "Server", "Both", "Neither". Default is "Both". |
| expirationTime | dateTime | no | Expiration time to execute the operation. The operation is executed if it is before the given expiration time. Otherwise, the operation will fail. In this case, "Operation expired" is returned as failure reason. |
Historic read
This operation reads history values and applies the mappings except of alarm mappings.
{
"deviceId": "<server-device-Id>",
"c8y_ua_command_HistoricReadOperation": {
"nodeId": "ns=2;s=MyLevel",
"processMappings": true,
"dateFrom": "2019-06-13T10:43:00+02:00",
"dateTo": "2019-06-13T10:52:00+02:00",
"tagType": "TAG",
"batchSize": 500
},
"description": "Historic read"
}
Available arguments for c8y_ua_command_HistoricReadOperation:
| Field | Type | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| nodeId | string | yes | ID of the node to execute the operation |
| dateFrom | dateTime | yes | The values are read starting from this time |
| dateTo | dateTime | yes | The values are read until this time |
| ranges | string | no | The index ranges of a subset of the multi-dimension array from the read attribute. The syntax is according to the OPC UA specification and will be transformed to NumericRange.
Example values to define the range for a 1D array is “0:1”, for a 2D array is “0:1,0:1” |
| batchSize | integer | no | Batch size for each history read call to the OPC UA server. Default is 200. |
| processMappings | Boolean | no | If set to false then the read values will not be processed based on the device protocol mapping. Default is true. Note that any data created from historic data using a device protocol will carry the same processing mode as specified in the mapping. |
| tagType | string | no | Possible tagType values are "TAG" and "NO_TAG". "TAG" appends "_Historic" for both the mapping types and for the measurement mappings. Default is "TAG". |
Historic data binary upload
This operation reads historic values and only saves those values to a file which can be retrieved using the binary API.
{
"deviceId": "<server-device-Id>",
"c8y_ua_command_HistoricDataUploadOperation": {
"nodeId": "ns=2;s=MyLevel",
"dateFrom": "2019-01-03T09:53:00+02:00",
"dateTo": "2019-06-13T18:53:00+02:00",
"chunkSize": 1,
"compress": true,
"batchSize": 150000
},
"description": "Upload history data"
}
The binary file representations, which can be queried using binary API, are created with the type “c8y_ua_HistoricData” and an operationId with the value of the operation with which it has been generated.
Available arguments for c8y_ua_command_HistoricDataUploadOperation:
| Field | Type | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| nodeId | string | yes | ID of the node to execute the operation |
| dateFrom | dateTime | yes | The values are read starting from this time |
| dateTo | dateTime | yes | The values are read until this time |
| ranges | string | no | The index ranges of a subset of the multi-dimension array from the read attribute. The syntax is according to the OPC UA specification and will be transformed to NumericRange.
Example values to define the range for a 1D array is “0:1”, for a 2D array is “0:1,0:1” |
| batchSize | integer | no | Batch size for each history read call to the OPC UA server. Default is 100000. |
| chunkSize | integer | no | The maximum file size in Mb for the output binary file. For each batch, the files can be divided based on this limit. |
| compress | Boolean | no | If set the false the output chunks are compressed. Default is false. |
Read file
Prerequisites:
- Open and Read methods for the file node must be implemented on server side, either as the children of the file node itself or as the children of the data type node
With this operation, a file can be downloaded from the OPC UA server at the given fileNodeId.
{
"deviceId" : "DEVICE_ID",
"c8y_ua_command_ReadFileOperation": {
"fileNodeId": "ns=2;s=sampleFile",
"bufferSize": <bufferSize>
},
"description":"Read sample file"
}
Available arguments for c8y_ua_command_ReadFileOperation:
| Field | Type | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| fileNodeId | string | yes | ID of the node to execute the operation |
| bufferSize | long | no | Maximum value can be 10 MB. The default size, if not set in the request, is 1MB. This will not limit the size of the file to be read. If the size is bigger, multiple read operations are triggered. |
| skipResetPosition | Boolean | no | If set to true then the position to read the file is reset before reading the file. Default is false. |
After the downloaded file has been read successfully (see Control tab of the device) it is available in Management > Files repository in the Administration application for download to local file system.
Alternatively, you can check the binary folder by using the binary API like this:
{{url}}/inventory/binaries
This returns a JSON response like this:
{
"self": "http://<tenant-domain>/inventory/binaries?pageSize=5¤tPage=1",
"managedObjects": [
{
"owner": <device-owner>,
"type": "ua-file-type",
"lastUpdated": "2021-05-17T14:33:21.074Z",
"name": "ns=2;s=sampleFile",
"self": "http://<tenant-domain>/inventory/binaries/2351",
"id": "2351",
"c8y_IsBinary": "",
"length": 13268,
"contentType": "application/octet-stream"
}
],
"statistics": {
"totalPages": 1,
"currentPage": 1,
"pageSize": 5
}
}
Now download is possible with the self link provided inside the managedObjects section of the JSON response.
For further information, refer to the Binaries API in the Cumulocity IoT OpenAPI Specification.
Write value
This operation writes values to the node/nodes.
{
"deviceId": "<server-device-Id>",
"c8y_ua_command_WriteValue": {
"values": {
"ns=3;s=LocalizedText": {
"value": "This is a localized text"
},
"ns=3;s=Double": {
"value": "3.14159"
}
}
},
"description": "Write values to different nodes"
}
Available arguments for c8y_ua_command_WriteValue:
| Field | Type | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| values | map<string, rangedValue> | yes | Map with ID of the node to execute the operation and RangedValue to set |
| expirationTime | dateTime | no | Expiration time to execute the operation. The operation is executed if it is before the given expiration time. Otherwise, the operation will fail. In this case, "Operation expired" is returned as failure reason. |
Available arguments for type rangedValue (used as map value in c8y_ua_command_WriteValue.values):
| Field | Type | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| value | string | yes | Value to set to the node attribute |
| ranges | string | no | The index ranges of a subset of the multi-dimension array. The syntax for the ranges is according to the OPC UA specification and will be transformed to NumericRange.
Example values to define the range for a 1D array is “0:1”, for a 2D array is “0:1,0:1” |
Write attribute
This operation is similar to the previous one, but instead of writing to the value attribute, this operation writes attributes' values to any writable attributes. The following example writes two different attributes to two different nodes.
{
"deviceId": "<server-device-Id>",
"c8y_ua_command_WriteAttribute": {
"values": {
"ns=3;s=LocalizedText": {
"attribute": "13",
"value": "This is a localized text"
},
"ns=3;s=Double": {
"attribute": "13",
"value": "3.14159"
}
}
},
"description": "Write attributes' values to different attributes of different nodes"
}
Available arguments for c8y_ua_command_WriteAttribute:
| Field | Type | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| values | map<string, attributeRangedValue> | yes | Map with ID of the node to execute the operation and AttributeRangedValue to set |
| expirationTime | dateTime | no | Expiration time to execute the operation. The operation is executed if it is before the given expiration time. Otherwise, the operation will fail. In this case, "Operation expired" is returned as failure reason. |
Available arguments for type attributeRangedValue (used as map value in c8y_ua_command_WriteAttribute.values):
| Field | Type | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| attribute | string | yes | ID of the attribute according to the OPC UA specification |
| value | string | yes | Value to set to the node attribute |
| ranges | string | no | The index ranges of a subset of the multi-dimension array. The syntax for the ranges is according to the OPC UA specification and will be transformed to NumericRange.
Example values to define the range for a 1D array is “0:1”, for a 2D array is “0:1,0:1” |
Example operation with ranges fragment:
{
"deviceId": "<server-device-Id>",
"c8y_ua_command_WriteAttribute": {
"values": {
"ns=3;s=FloatArray": {
"attribute": "13",
"ranges": "0:1",
"value": "2.0,4.0"
}
}
},
"description": "Write attribute value to array attribute"
}
Get method description
This operation reads the description of a method node.
{
"deviceId": "<server-device-Id>",
"c8y_ua_command_GetMethodDescriptionOperation": {
"nodeId": "ns=2;s=MyMethod"
},
"description": "get method description"
}
Available arguments for c8y_ua_command_GetMethodDescriptionOperation:
| Field | Type | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| nodeId | string | yes | ID of the node to execute the operation |
The result describes a method, it’s parent object, input and output arguments.
{
"nodeId": "ns=2;s=MyMethod",
"name": "MyMethod",
"parentNodeId": "ns=2;s=MyDevice",
"parentName": "MyDevice",
"inputArguments": [{
"name": "Operation",
"description": "The operation to perform on parameter: valid functions are sin, cos, tan, pow",
"dataType": "String",
"dataTypeId": "i=12"
},
{
"name": "Parameter",
"description": "The parameter for operation",
"dataType": "Double",
"dataTypeId": "i=11"
}
],
"outputArguments": [{
"name": "Result",
"description": "The result of 'operation(parameter)'",
"dataType": "Double",
"dataTypeId": "i=11"
}]
}
Call method
This operation calls the method on the OPC UA server. It requires complete input arguments with an additional “value” fragment.
{
"deviceId": "<server-device-Id>",
"c8y_ua_command_CallMethodOperation": {
"request": {
"nodeId": "ns=2;s=MyMethod",
"arguments": [{
"name": "Operation",
"description": "The operation to perform on parameter: valid functions are sin, cos, tan, pow",
"dataType": "String",
"dataTypeId": "i=12",
"value": "pow"
},
{
"name": "Parameter",
"description": "The parameter for operation",
"dataType": "Double",
"dataTypeId": "i=11",
"value": "5"
}
]
}
},
"description": "call method"
}
Available arguments for c8y_ua_command_CallMethodOperation:
| Field | Type | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| request | methodRequest | yes | Request to send to the OPC UA Server |
| expirationTime | dateTime | no | Expiration time to execute the operation. The operation is executed if it is before the given expiration time. Otherwise, the operation will fail. In this case, "Operation expired" is returned as failure reason. |
Available arguments for type methodRequest (used in c8y_ua_command_CallMethodOperation.request):
| Field | Type | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| nodeId | string | yes | ID of the node to execute the operation |
| arguments | list<methodArgument> | no | List of arguments for the method request |
| objectNodeId | string | no | The NodeId of the Object or ObjectType that is the source of a HasComponent reference (or subtype of HasComponent reference) to the method |
| parseResponse | Boolean | no | If set to true, the value is converted to JSON and the actual value is stored in the rawValue fragment in response. Default is true |
Available arguments for type methodArgument (used in c8y_ua_command_CallMethodOperation.request.arguments):
| Field | Type | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| name | string | no | Name of the method argument |
| description | string | no | Description of the method argument |
| dataType | string | yes | Data type of the method argument |
| dataTypeId | string | yes | ID of the data type in OPC UA Server |
| value | string | yes | Value for the method argument |
| arrayDimension | string | no | Array dimension for the value to set if the value is an array |
The result contains all output arguments with values set by the OPC UA server. Power of 5 is 25:
{
"statusCode": 0,
"result": [{
"name": "Result",
"description": "The result of 'operation(parameter)'",
"dataType": "Double",
"dataTypeId": "i=11",
"value": "25.0"
}]
}
Testing a device type against a node on an OPC UA server
This operation allows for testing a device type against a specific node on an OPC UA server. The operation result provides diagnostic information if the device type could be applied:
{
"deviceId":"<server-device-Id>",
"c8y_ua_command_TestDeviceTypeMatching":{
"deviceTypeId":"<device-type-id>",
"rootNodeId":"<node-id>"
},
"description":"Test Device Type"
}
Available arguments for c8y_ua_command_TestDeviceTypeMatching:
| Field | Type | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| deviceTypeId | string | yes | ID of the managed object containing the device protocol |
| rootNodeId | string | yes | ID of the root node to execute the operation |
If the device type can be applied to the given node, the operation result confirms this:
{
"creationTime":"2020-08-20T12:28:57.973Z",
"deviceId":"12789",
"deviceName":"Test Server",
"id":"15478",
"status":"SUCCESSFUL",
"c8y_ua_command_TestDeviceTypeMatching":{
"deviceTypeId":"14989",
"rootNodeId":"nsu=urn:cumulocity:opcua:test:server;s=HelloWorld/Dynamic2"
},
"c8y_Command":{
"result":"{\n \"matches\": true\n}"
},
"description":"Test Device Type"
}
Otherwise, the operation result provides an explanation why the device type could not be matched to the given root node:
{
"creationTime":"2020-08-20T12:34:01.524Z",
"deviceId":"12789",
"deviceName":"Milo Reloaded",
"id":"15688",
"status":"SUCCESSFUL",
"c8y_ua_command_TestDeviceTypeMatching":{
"deviceTypeId":"14989",
"rootNodeId":"nsu=urn:cumulocity:opcua:test:server;s=HelloWorld/Dynamic9"
},
"c8y_Command":{
"result":"{\n \"matches\": false,\n \"reason\": \"Does not match browse path regex constraint, constraints: (.*Dynamic[1-3]), actual: [[http://opcfoundation.org/UA/:Root, http://opcfoundation.org/UA/:Objects, urn:cumulocity:opcua:test:server:Dynamic Playground, urn:cumulocity:opcua:test:server:Dynamic9]]\"\n}",
"syntax":null,
"text":null
},
"description":"Test Device Type"
}
Analyzing the set of nodes to which a device type can be applied (dry run)
As explained earlier, the Cumulocity IoT OPC UA gateway performs an auto-discovery to determine the set of nodes that match a certain device protocol (“device type”). The following operation performs an auto-discovery for the given device protocol on the server, without actually applying it to any node (“dry run”):
{
"deviceId":"<server-device-Id>",
"c8y_ua_command_DryRunDeviceTypeMatching":{
"deviceTypeId":"<device-type-id>"
},
"description":"Dry Run Device Type"
}
Available arguments for c8y_ua_command_DryRunDeviceTypeMatching:
| Field | Type | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| deviceTypeId | string | yes | ID of the managed object containing the device protocol |
The result of the operation contains the set of nodes that match the device protocol. In addition to that, the fragment matchednodes is added to the operation. It contains a JSON representation of the matched nodes.
{
"creationTime":"2020-08-20T12:22:07.947Z",
"deviceId":"12789",
"deviceName":"Test Server",
"id":"15187",
"status":"SUCCESSFUL",
"c8y_Command":{
"result":"Device protocol is currently disabled. Device protocol would be applied to the following nodes: [\n {\n \"nodeId\": \"nsu=urn:cumulocity:opcua:test:server;s=HelloWorld/Dynamic2\",\n \"deviceTypeId\": \"14989\",\n \"mappedTargetNodes\": [\n {\n \"browsePath\": [\n \"urn:cumulocity:opcua:test:server:Double\"\n ],\n \"targetNodeId\": \"nsu=urn:cumulocity:opcua:test:server;s=HelloWorld/Dynamic/Double2\"\n }\n ],\n \"attrs\": {}\n },\n {\n \"nodeId\": \"nsu=urn:cumulocity:opcua:test:server;s=HelloWorld/Dynamic1\",\n \"deviceTypeId\": \"14989\",\n \"mappedTargetNodes\": [\n {\n \"browsePath\": [\n \"urn:cumulocity:opcua:test:server:Double\"\n ],\n \"targetNodeId\": \"nsu=urn:cumulocity:opcua:test:server;s=HelloWorld/Dynamic/Double1\"\n }\n ],\n \"attrs\": {}\n },\n {\n \"nodeId\": \"nsu=urn:cumulocity:opcua:test:server;s=HelloWorld/Dynamic3\",\n \"deviceTypeId\": \"14989\",\n \"mappedTargetNodes\": [\n {\n \"browsePath\": [\n \"urn:cumulocity:opcua:test:server:Double\"\n ],\n \"targetNodeId\": \"nsu=urn:cumulocity:opcua:test:server;s=HelloWorld/Dynamic/Double3\"\n }\n ],\n \"attrs\": {}\n }\n]",
"matchedNodes":[
{
"mappedTargetNodes":[
{
"targetNodeId":"nsu=urn:cumulocity:opcua:test:server;s=HelloWorld/Dynamic/Double2",
"browsePath":[
"urn:cumulocity:opcua:test:server:Double"
]
}
],
"deviceTypeId":"14989",
"nodeId":"nsu=urn:cumulocity:opcua:test:server;s=HelloWorld/Dynamic2"
},
{
"mappedTargetNodes":[
{
"targetNodeId":"nsu=urn:cumulocity:opcua:test:server;s=HelloWorld/Dynamic/Double1",
"browsePath":[
"urn:cumulocity:opcua:test:server:Double"
]
}
],
"deviceTypeId":"14989",
"nodeId":"nsu=urn:cumulocity:opcua:test:server;s=HelloWorld/Dynamic1"
},
{
"mappedTargetNodes":[
{
"targetNodeId":"nsu=urn:cumulocity:opcua:test:server;s=HelloWorld/Dynamic/Double3",
"browsePath":[
"urn:cumulocity:opcua:test:server:Double"
]
}
],
"deviceTypeId":"14989",
"nodeId":"nsu=urn:cumulocity:opcua:test:server;s=HelloWorld/Dynamic3"
}
],
"syntax":null,
"text":null
},
"description":"Dry Run Device Type",
"c8y_ua_command_DryRunDeviceTypeMatching":{
"deviceTypeId":"14989"
}
}
Get the current application state of a device type
In order to know what is the current state of a device type application, use the following operation:
{
"description": "Get device type application state",
"deviceId": "{server ID}",
"c8y_ua_command_GetDeviceTypeApplicationState": {
"deviceTypeId": "{device protocol ID}",
"matchingRootNodes": ["{root node ID #1}", "{root node ID #2}"]
}
}
Available arguments for c8y_ua_command_GetDeviceTypeApplicationState:
| Field | Type | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| deviceTypeId | string | yes | ID of the managed object containing the device protocol |
| matchingRootNodes | list<string> | no | List of ID of the root nodes to execute the operation. When it is not provided, the application state of all matching nodes will be returned. |
The result will be populated into the operation result as a map of nodes telling whether the device type has been applied to that node or not.
Sample result when the device type has been applied to node #1 but not node #2:
{
"{root node ID #1}": true,
"{root node ID #2}": false
}
Expiring operations
In certain cases it is desirable that the OPC UA gateway executes an operation only if it processes it before a given expiration time. Providing such an optional expiration time is supported for the following OPC UA operations:
- Reading the value of a node/nodes
- Reading all attributes of a node
- Reading an attribute
- Read complex
- Write value
- Write attribute
- Call method
For all the given operations this expiry mechanism can be activated by supplying an expirationTime fragment inside the operation body.
The following example shows how to mark a read operation as expiring:
{
"deviceId" : "<server-device-Id>",
"c8y_ua_command_ReadValue": {
"nodes": ["ns=3;s=FloatArray"],
"expirationTime": "2021-02-08T15:00:00.000Z"
},
"description":"Expiring read value"
}
The operation above will only perform a read on the OPC UA server if processed by the gateway before the 8th of February, 2021 15:00. Otherwise, the operation will fail. In this case, Operation expired is returned as failure reason.
OPC UA events
Model change events
The model change events are created by the OPC UA server to notify about the changes in an address space node on runtime.
The gateway subscribes to the events of type BaseModelChangeEventType on connection to the servers. The subscription to this event can be enabled or disabled for each server
using the subscribeModelChangeEvent property during the server configuration. The changes for the events with type GeneralModelChangeEventType and SemanticChangeEventType, which are subtypes
of BaseModelChangeEventType, are handled and address space information is persisted in the Cumulocity IoT inventory as well as in the local address space file of the gateway.
Troubleshooting
Permission denied error when running the gateway JAR file on a Linux OS
If the following error appears, add a baseDir property to the YAML file. For example:
db:
baseDir: ${user.home}/.opcua/profile/data
Unknown host exception when running the gateway JAR
This error appears if the provided baseUrl property in the YAML file is incorrect.
Failed to load property source from location when running the gateway JAR
The following error appears if the indentation of the properties in the YAML file is incorrect.
java.net.BindException: Address already in use
If this error appears, a Java process is running in the background. To fix this issue, the process must be stopped/killed.
Changing the log level for troubleshooting
For troubleshooting purposes, we recommend you to enable the DEBUG log level for subpackages and root if required, and send the log file to product support.
For example:
<logger name="com.cumulocity.opcua.client.gateway" level="DEBUG"/>
<logger name="com.cumulocity" level="DEBUG"/>
<logger name="c8y" level="DEBUG"/>
<root level="DEBUG">
<appender-ref ref="FILE" />
<appender-ref ref="STDOUT"/>
</root>
If there is an unknown error during the address space scans, enable DEBUG or TRACE log level specifically for the scanners:
<logger name="com.cumulocity.opcua.client.BaseAddressSpaceScanner" level="DEBUG" />
<logger name="com.cumulocity.opcua.client.OpcuaAddressSpaceFullScanner" level="DEBUG" />
<logger name="com.cumulocity.opcua.client.OpcuaAddressSpaceLightScanner" level="DEBUG" />
<logger name="com.cumulocity.opcua.client.OpcuaAddressSpaceReverseFullScanner" level="DEBUG" />
<root level="INFO">
<appender-ref ref="FILE" />
<appender-ref ref="STDOUT"/>
</root>
For additional information about log levels, refer to the Logback architecture documentation.
Java Management Extensions (JMX)
For additional monitoring, the gateway component provides MBeans. These MBeans get exposed if the following configuration is set in the application.yaml file:
spring:
jmx:
enabled: true
Via jconsole the MBeans can be selected and the following attributes can be accessed:
It can be useful to get some statistics for custom actions in particular. These attributes can be retrieved from the CustomActionMBean:
-
Table of all called URLs seperated by HTTP return code and retry count.
The key entry of the table consists of:
{URL}_{HTTP Response Code}_{Retry Count} -
If retry is enabled, the queue size of the retry queue can be monitored.