Running Cumulocity IoT DataHub on Cumulocity IoT Edge
This section describes how to run Cumulocity IoT DataHub on the Cumulocity IoT Edge, the local version of Cumulocity IoT.
This section describes how to run Cumulocity IoT DataHub on the Cumulocity IoT Edge, the local version of Cumulocity IoT.
The following sections will walk you through all the functionalities of Cumulocity IoT DataHub Edge in detail.
For your convenience, here is an overview of the contents:
| Section | Content |
|---|---|
| Cumulocity IoT DataHub Edge overview | Get an overview of Cumulocity IoT DataHub Edge |
| Setting up Cumulocity IoT DataHub Edge | Set up Cumulocity IoT DataHub Edge and its components |
| Working with Cumulocity IoT DataHub Edge | Manage offloading pipelines and query the offloaded results |
| Operating Cumulocity IoT DataHub Edge | Run administrative tasks |
Cumulocity IoT Edge is an onsite, single-server, and single-tenant variant of the Cumulocity IoT Core platform. It is delivered as a software appliance designed to run on industrial PCs or local servers. Cumulocity IoT DataHub is available as an add-on to Cumulocity IoT Edge.
Cumulocity IoT DataHub Edge offers the same functionality as the cloud-variant of Cumulocity IoT DataHub, but stores the data locally. You can define offloading pipelines, which regularly move data from the Operational Store of Cumulocity IoT into a data lake. In the Edge setup, a NAS is used as data lake. Dremio, the internal engine of Cumulocity IoT DataHub, can access the data lake and run analytical queries against its contents, using SQL as the query interface.
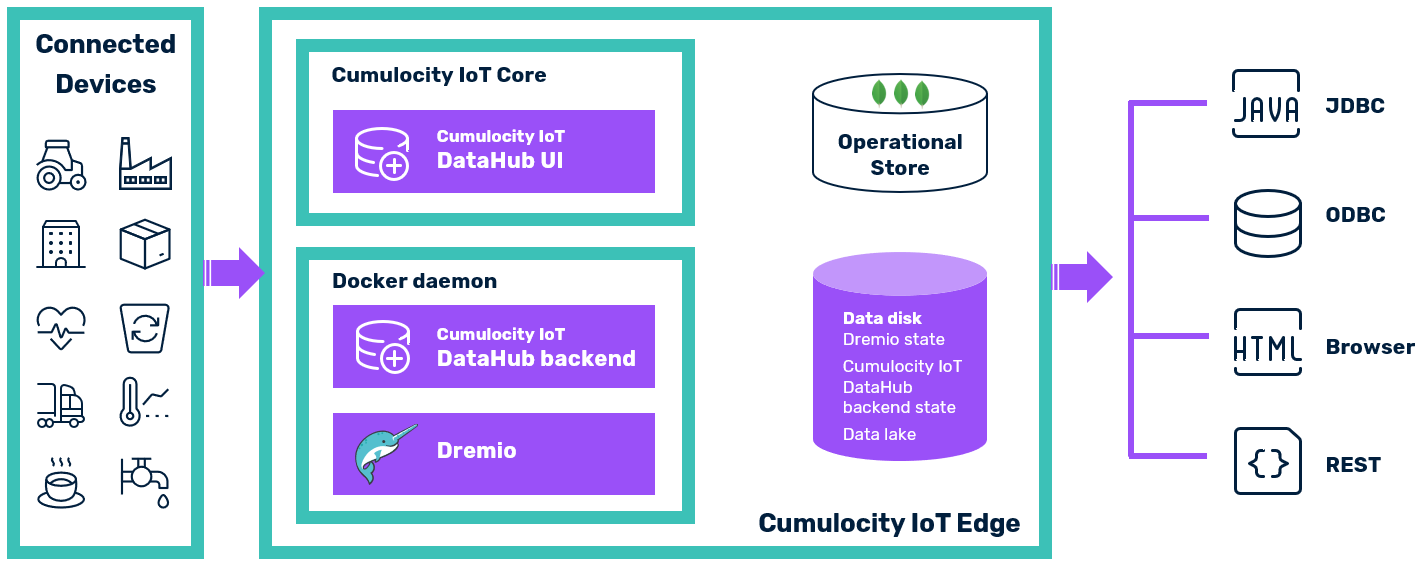
Cumulocity IoT DataHub Edge consists of the following building blocks:
Cumulocity IoT DataHub Edge uses the same software as Cumulocity IoT DataHub, though in the following aspects these two variants differ:
| Area | Cumulocity IoT DataHub Edge | Cumulocity IoT DataHub Cloud |
|---|---|---|
| High Availability | Depending on the underlying virtualization technology | Depending on the cloud deployment setup |
| Vertical scalability | Yes | Yes |
| Horizontal scalability | No | Yes |
| Upgrades with no downtime | No | No |
| Root access | No | Yes, if customer is hosting |
| Installation | Offline | Online |
| Dremio cluster setup | 1 master, 1 executor | Minimum 1 master, 1 executor |
| Dremio container management | Docker daemon | Kubernetes |
| Cumulocity IoT DataHub backend container management | Docker daemon | Microservice in Cumulocity IoT Core |
| Data lakes | NAS | Azure Storage, S3, HDFS, (NAS) |
Before setting up Cumulocity IoT DataHub Edge, you must check the following prerequisites:
| Item | Details |
|---|---|
| Cumulocity IoT Edge | The local version of Cumulocity IoT is set up on a Virtual Machine (VM). See also section Setting up Cumulocity IoT Edge. |
| Cumulocity IoT DataHub Edge archive | You have downloaded the archive with all installation artifacts from the Software AG Empower Portal. |
| Internet access | Internet access is not required. |
The hardware requirements for running a bare Cumulocity IoT Edge instance are described in section Requirements. When Cumulocity IoT DataHub Edge is additionally running, the hardware requirements of the virtual machine are as follows:
Hardware requirements for the host OS are excluded.
Copy the Cumulocity IoT DataHub Edge archive to the Cumulocity IoT Edge.
scp datahub-edge.tar admin@<edge_ip_address>:/tmp
Log in as admin into Cumulocity IoT Edge.
ssh admin@<edge_ip_address>
Run the install script.
sudo /opt/c8y/utilities/install_signed_package.sh /tmp/datahub-edge.tar
During script execution, you are prompted for the username and password of the administration user of the tenant edge. During installation, you are also prompted to set the new password of the Dremio admin account. It takes a few minutes to complete the installation. After completion you can delete the Cumulocity IoT DataHub Edge archive.
The install script runs the following basic steps:
The Docker containers will be restarted automatically if the container itself fails or the applications within are no longer reachable.
The containers are configured to store their application state on the data disk under /opt/mongodb:
An upgrade of Cumulocity IoT DataHub Edge follows the same steps as the initial setup. First, you must copy the archive with the new version to Cumulocity IoT Edge. Next, you must log in as admin. Then you must run the install script using the new version.
sudo /opt/c8y/utilities/install_signed_package.sh /tmp/datahub-<NEW version>.tar
During script execution, the already installed version is detected and the script runs an upgrade using the new version. It takes a few minutes to complete the installation. After completion you can delete the Cumulocity IoT DataHub Edge archive.
There might be cases where you must change the network setup of your Edge installation, for example by setting the IP range used by Edge internally or changing the domain name. The network configuration of Cumulocity IoT DataHub Edge must be adapted to such a change by running the script /opt/softwareag/cdh/bin/restart.sh once. The script restarts Cumulocity IoT DataHub with parameters aligned with the new network configuration.
The different Cumulocity IoT DataHub Edge interfaces can be accessed in the same way as in a cloud deployment of Cumulocity IoT DataHub.
| Interface | Description |
|---|---|
| Cumulocity IoT DataHub Edge UI | The UI can be accessed in the application switcher after you have logged into the Cumulocity IoT Edge UI. Alternatively you can access it directly under http://edge_domain_name/apps/datahub-ui or https://edge_domain_name/apps/datahub-ui, depending on whether TLS/SSL is used or not. A login is required as well, with "edge" being used as tenant name. |
| Dremio UI | On the Cumulocity IoT DataHub Edge home page you will find a link to the Dremio UI. Alternatively you can access it directly under http://datahub.edge_domain_name or https://datahub.edge_domain_name, depending on whether TLS/SSL is used or not. You can log in as admin using the password defined in the installation procedure. |
| Cumulocity IoT DataHub JDBC/ODBC | You find the connection settings and the required driver version for JDBC/ODBC in the Cumulocity IoT DataHub Edge UI on the Home page. |
| Cumulocity IoT DataHub REST API | The path of the microservice which hosts the API is https://edge_domain_name/service/datahub. |
| Dremio REST API | The Dremio URL to run REST API requests against is either http://datahub.edge_domain_name or https://datahub.edge_domain_name, depending on whether TLS/SSL is used or not. |
The definition and assignment of permissions and roles is done in the same way as in a cloud deployment. See the section Defining Cumulocity IoT DataHub permissions and roles for details.
The setup of the Dremio account and the data lake is done in the same way as in a cloud deployment. See the section Setting up Cumulocity IoT DataHub for details.
Cumulocity IoT DataHub Edge is configured to use a NAS as data lake. When configuring the NAS use as mount path /datalake. This path is mounted to /opt/mongodb/cdh-master/datalake.
Depending on the use case, it might be necessary to increase the memory available to Dremio, the internal engine of Cumulocity IoT DataHub. By default, Dremio is configured to consume a maximum of 4 GB of RAM (2 GB assigned to both master node and executor node).
Depending on the situation, one either needs to increase the memory of Dremio’s master or executor node. In many cases, the master node’s memory is the limiting factor, but not always. Inspecting the query profiles in Dremio helps to determine where the bottleneck occurs.
Run the following steps:
vi /etc/cdh/cdh-master/dremio-env and change DREMIO_MAX_HEAP_MEMORY_SIZE_MB=1750 and DREMIO_MAX_DIRECT_MEMORY_SIZE_MB=250 to your needs. For example, you can double both values.service cdh-master restart.Run the following steps:
vi /etc/cdh/cdh-executor/dremio-env and change DREMIO_MAX_HEAP_MEMORY_SIZE_MB=1024 and DREMIO_MAX_DIRECT_MEMORY_SIZE_MB=1488 to your needs. For example, you can double both values.service cdh-executor restart.Cumulocity IoT DataHub Edge offers the same set of functionality as the cloud variant. See the section Working with Cumulocity IoT DataHub for details on configuring and monitoring offloading jobs, querying offloaded Cumulocity IoT data, and refining offloaded Cumulocity IoT data.
Similar to the cloud variant, Cumulocity IoT DataHub Edge UI allows you to check system information and view audit logs. See the section on Operating Cumulocity IoT DataHub for details.
When managing Cumulocity IoT DataHub Edge, the following standard tasks are additionally relevant.
If problems occur, you should follow these steps:
If you need to contact product support, include the output of the diagnostics script. See the section on Diagnostics and support > Diagnostics in the Cumulocity IoT Edge guide for details of how to run it.
You can check the status of the backend in the Administration page of the Cumulocity IoT DataHub UI. Alternatively you can query the isalive endpoint, which should produce an output similar to:
curl --user admin:your_password https://edge_domain_name/service/datahub/isalive
{
"timestamp" : 1582204706844,
"version" : {
"versionId" : "10.6.0.0.337",
"build" : "202002200050",
"scmRevision" : "4ddbb70bf96eb82a2f6c5e3f32c20ff206907f43"
}
}
If the backend cannot be reached, you will get an error response.
You can check the status of Dremio using the server_status endpoint:
curl http://datahub.edge_domain_name/apiv2/server_status
"OK"
Dremio is running if OK is returned. No response will be returned if it is not running or inaccessible.
The installation log file is stored at /var/log/cdh.
In order to access the logs of the Cumulocity IoT DataHub and Dremio containers, you must use the Docker logs command. To follow the logs of cdh-master you must run:
docker logs -f cdh-master
To follow the logs of cdh-executor you must run:
docker logs -f cdh-executor
The containers are configured to rotate log files with rotation settings of two days and a maximum file size of 10 MB.
Cumulocity IoT Edge uses Monit for management and monitoring of relevant processes. See the section on Diagnostics and support > Monitoring in the Cumulocity IoT Edge guide for details. The Cumulocity IoT DataHub Edge processes, namely the Cumulocity IoT DataHub backend and the Dremio nodes, are also monitored by Monit.
The data disk is used for storing the state of Cumulocity IoT DataHub and Dremio and serves as data lake. In order to ensure that the system can work properly, the disk must not run out of space. The main factors for the disk space allocation of Cumulocity IoT DataHub Edge are the Dremio job profiles and the data lake contents.
Dremio maintains a history of job details and profiles, which can be inspected in Dremio’s job log, that is, the “Jobs” page of the Dremio UI. This job history must be cleaned up regularly to free the resources necessary for storing it.
Dremio is configured to perform the cleanup of job results automatically without downtime. The default value for the maximum age of stored job results is seven days. To change that value, a Dremio administrator must modify the support key jobs.max.age_in_days. The changes become effective within 24 hours or after restarting Dremio. See the corresponding Dremio documentation for more details on support keys.
The data lake contents are not automatically purged, as the main purpose of Cumulocity IoT DataHub is to maintain a history of data. However, if disk space is critical and cannot be freed otherwise, parts of the data lake contents must be deleted.
Browse to the data lake folder /opt/mongodb/cdh-master/datalake. The data within the data lake is organized hierarchically. Delete the temporal folders you deem adequate to be deleted. After that you must run with the administrator account the following query in Dremio to refresh the metadata:
ALTER PDS <deleted_folder_path> REFRESH METADATA FORCE UPDATE
Cumulocity IoT DataHub’s runtime state as well as the data lake containing offloaded data reside in the Cumulocity IoT Edge server VM. In order to back up and restore Cumulocity IoT DataHub, its runtime state, and its data we recommend you to back up and recover the Cumulocity IoT Edge server VM as described in section Backup and restore.